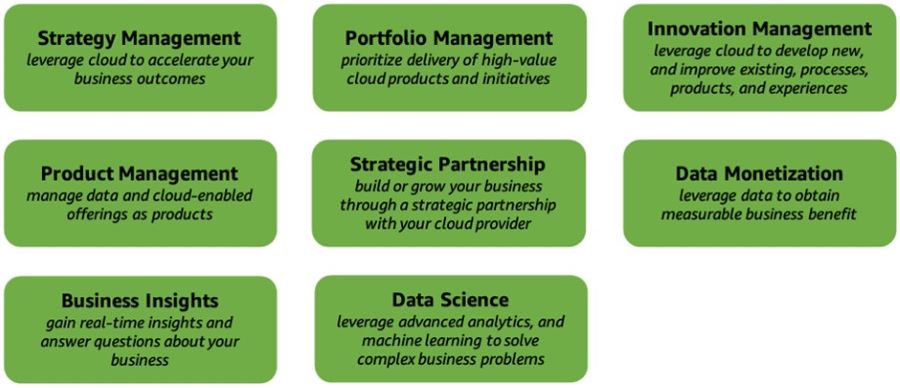
|
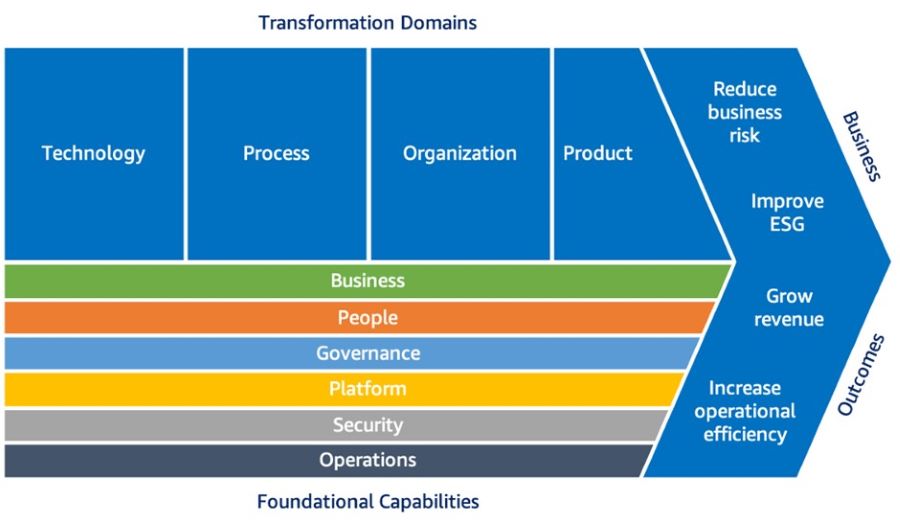
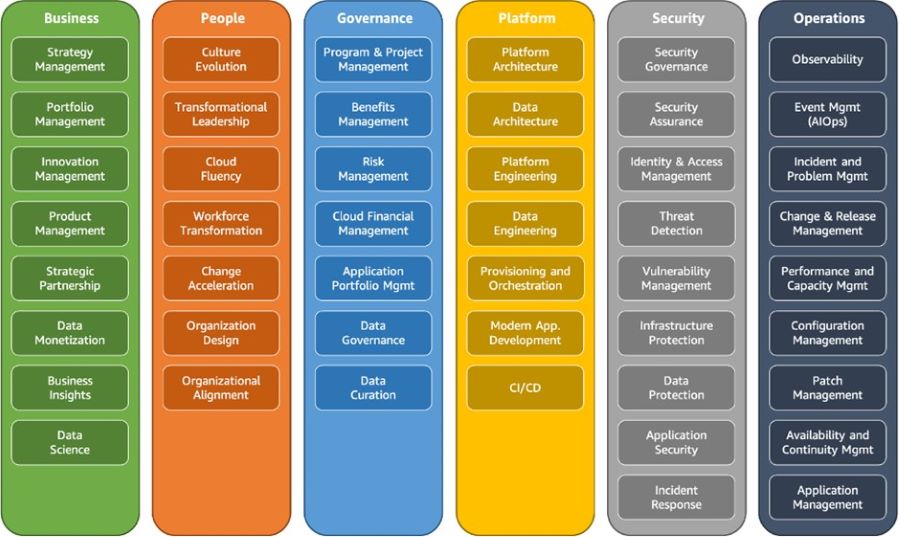
This article outlines the key principles for developing a successful cloud operating model (COM) that enables organizations to efficiently and securely adopt cloud solutions and drive business outcomes. Establishing an Effective COM Establishing a well-designed COM is crucial for the successful adoption of cloud technology within an organization. The impact of cloud adoption extends beyond just the IT department and has significant implications for the organizational culture and IT delivery structures. It is essential to understand these implications and the organization's readiness for change when building a successful COM. To facilitate this transformation, organizations need to have a sufficient number of individuals with experience in utilizing cloud services, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), who can effectively implement and manage the underlying cloud platform using a product-centric approach. Moving Beyond Traditional ApproachesMany organizations initially approach cloud adoption as an additional layer of technology within their existing operating model and infrastructure. While this approach may lead to cost savings and value through reduced infrastructure expenses compared to traditional on-premises solutions, it also presents challenges. One of the main concerns is that organizations may struggle to keep up with the pace of new business initiatives due to the complexity introduced by adding another technology layer. It often takes a significant event or issue to prompt IT leaders to take action and establish a dedicated Cloud team or a Center of Excellence (COE). AWS refer to this capability as a Cloud Enablement Engine (CEE). A CEE encompasses a combination of technology and business resources aimed at guiding the organization through its cloud adoption journey, addressing the most critical needs of the business as a whole, not just the IT department. This article discusses essential elements for establishing a successful cloud adoption capability and outlines mechanisms for accelerating the process before major events or issues occur. Additionally, it demonstrates how the AWS Domain model can help align the operating model with the most critical business needs. Prerequisites for Success To ensure the success of cloud adoption, the CEE should align with the organization's primary business objectives and outcomes. This ensures that the evaluation of cloud adoption success is measured in terms of the business benefits achieved and establishes the foundation for the operating model and task prioritization. An important prerequisite for success is obtaining endorsement from organizational leaders and securing executive sponsorship in the form of a Cloud Leadership Team. Successful cloud adopters challenge the existing norms within their organizations. Without this sponsorship and support, CEEs may face obstacles and encounter delays. In large organizations with multiple business units, it may be necessary to consider additional or alternative federated approaches, such as establishing a Community of Practice, rather than relying solely on a centralized team. Target Business Outcomes and Value When it comes to building and establishing a Cloud Operating Model (COM), the desired outcomes are not strictly defined like in some technical domains. My experience in working with successful cloud technology leaders, such as CIOs and CTOs, has shown that they prioritize the creation of a value-generating Cloud Enablement Engine (CEE) before encountering failures and firefighting scenarios. Here are some examples of value generation observed among AWS adopters:
The Focus on Technology and Reactive ResponsesUnfortunately, many IT leaders tend to focus solely on the technical aspects of cloud until issues arise, forcing them to take action and adopt different approaches. The most common issues that prompt such reactions are:
Enabling Innovation and Value with a Successful COM A successful COM empowers organizations to operate applications in the cloud with increased speed, innovation, and business value, all while maintaining reliability and security. A key aspect of leading COM approaches is the adoption of a product-based mindset for the cloud platform. By embracing this approach, each team takes ownership and responsibility for operational excellence, actively maintaining self-healing systems that quickly recover from failures through integrated detection and remediation mechanisms. Additionally, platform optimization can be achieved by measuring known application baselines and testing them using chaos engineering (failure injection) and game days (interactive team-based learning exercises). Cultural Shift and Automation Focus Implementing these recommendations often requires a cultural shift in how organizations design, deploy, and operate their cloud platforms. It involves prioritizing automation and establishing repeatable processes that enhance efficiency and reliability over time. Product-Based Delivery of CloudThe most successful cloud customers approach their cloud initiatives with a product mindset, prioritizing excellent customer experiences. In this context, a product is defined by its ability to perform a limited set of tasks exceptionally well, with clearly defined inputs and outputs, serving multiple customers and continuously evolving to meet their needs. An example of this approach can be seen in Amazon.com, where multiple product teams manage different aspects of the customer website. Defining products is crucial as it establishes the relationship between customers (consumers), products, and the teams responsible for creating them (suppliers). These interdependencies highlight the dual role of product teams as both consumers and suppliers, necessitating a higher level of ownership, accountability, and scrutiny to ensure the delivery of high-quality products and services. Benefits of a Product-Based Approach When companies fail to define and operate their systems as products, they often experience foundational failures that could have been mitigated through cross-product accountability. By assigning end-to-end ownership and accountability to each product team, encompassing business and operational aspects, they become fully responsible for all aspects of their services. Even shared service providers act as product owners, offering services that other product teams can choose to use. It's important to note that the demand for each product should be assessed, and those that are not useful to the business should be deprioritized. The primary outcome is that each product team maintains accountability and doesn't relinquish responsibility to other product suppliers. Building Customer Empathy and Trust By taking full ownership of a product's operation and considering the end customer's perspective, companies cultivate empathy and understanding. As product owners establish contracts with other product owners, a supplier-consumer relationship is formed, fostering trust. Empowering product teams to make decisions about problem-solving approaches and choosing other products they collaborate with ensures full accountability for the product's performance and customer perception. Key Concepts for a Product Mindset To foster a functional product mindset and minimize future events that impact customers, four foundational concepts are crucial:
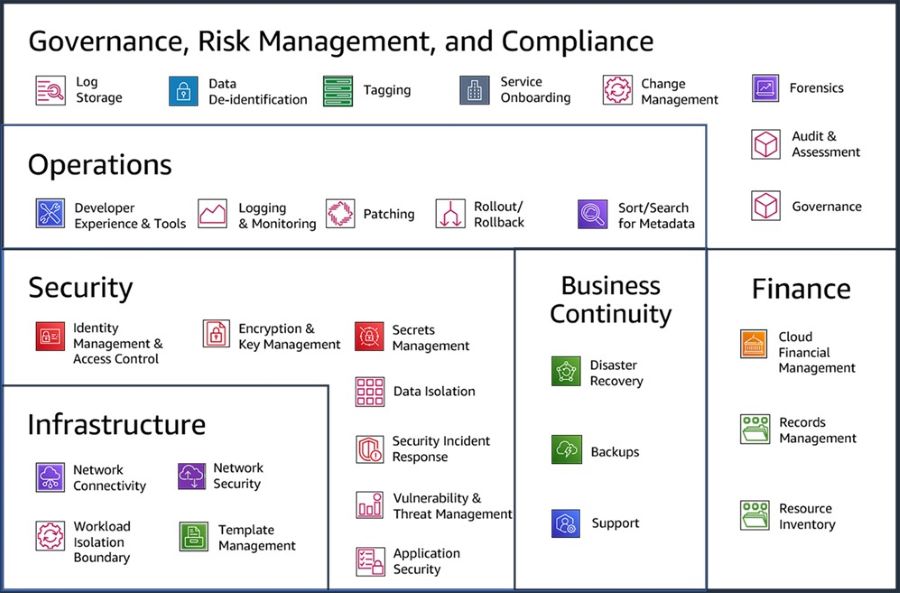
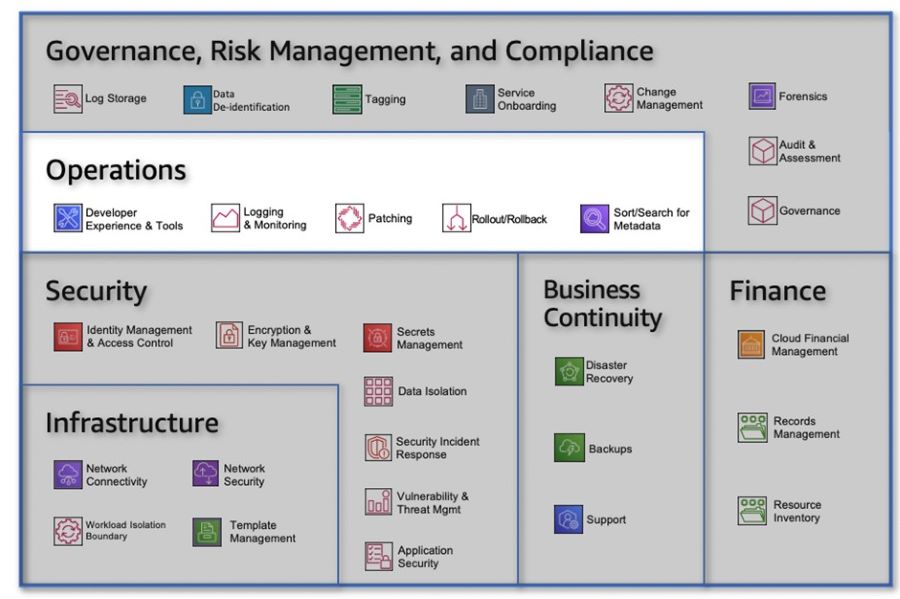
Summary of ActivitiesSeveral key activities can facilitate and accelerate cloud adoption and the delivery of business outcomes. In enterprises, competing priorities often exist within their cloud strategy. Failure to transform operating models can result in a phenomenon known as the "great stall," where adoption momentum slows or halts. Establishing a cloud delivery and governance function, often referred to as a Cloud Center of Excellence (CCoE) or Cloud Enablement Engine (CEE), has proven to be a significant factor in avoiding this effect. This document outlines six steps that companies should follow to build a successful CEE:
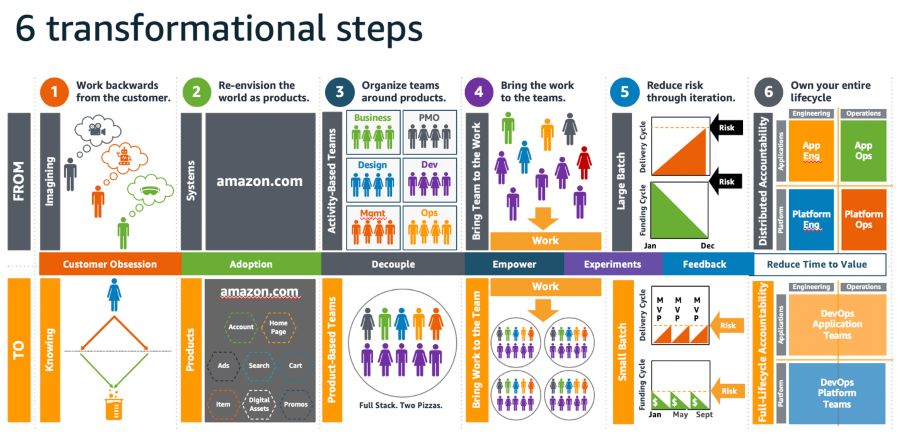
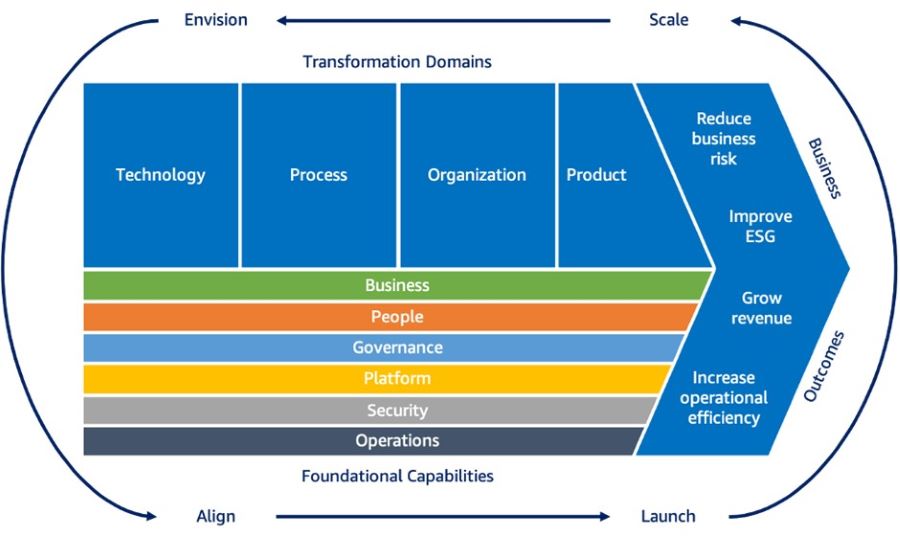
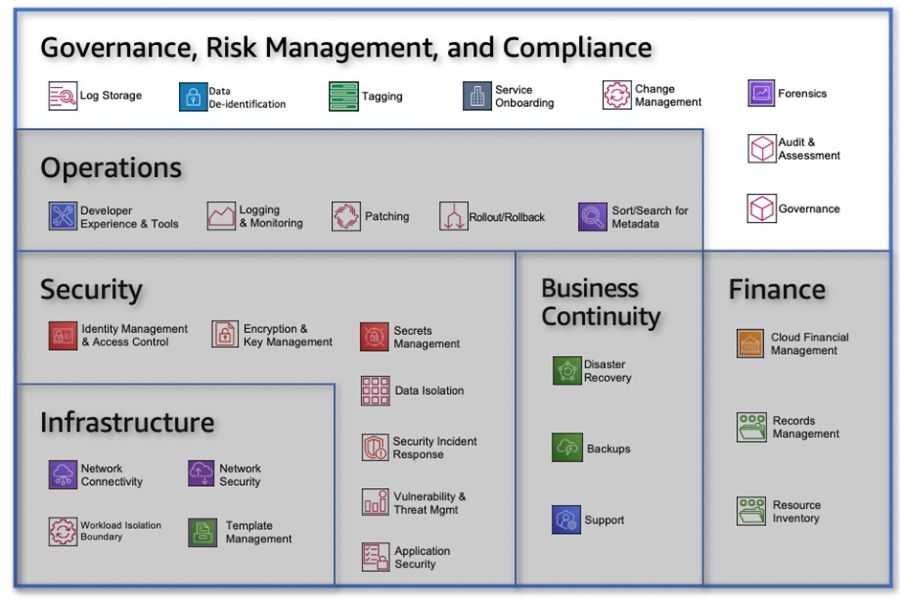
Figure 1: Six transformational steps for building a cloud operating model Step 1: Work Backwards from the CustomerIn order to build successful Cloud Operating Models (COMs), it is crucial to deliver innovative, cost-effective, reliable, and secure solutions that accelerate business outcomes for organizational business units. Many companies often make guesses or assumptions about what their customers want, relying on imagination or hunches. However, this approach increases the likelihood of being wrong. To truly be customer-centric or customer-obsessed, teams need to move from imagining to knowing. This involves dedicating time to understanding customers, identifying their delights and pain points. Data should be leveraged to prove a deep understanding of customers and their needs. Then, the focus should be on finding the best solutions to address their pain points, gradually narrowing down the options until the simplest and most effective solution emerges. Balancing Core COM Capabilities A Cloud Enablement Engine (CEE) should prioritize core COM capabilities while striking a balance between innovation and security. Reliability is essential, but it's important for organizations to operate and invest within their budget constraints. AWS helps customers achieve this balance by aligning the delivery to their Cloud Adoption Framework (CAF), which draws from the best practices of cloud transformations accumulated over many years. Figure 2: The AWS Cloud Adoption Framework - Capabilities and Domains Connecting Business Goals to Business and Technology Enablers Many cloud adoptions start from a highly technical perspective. By utilizing a combination of the working backwards and envisioning processes, AWS helps establish a foundation for a cloud strategy and operating model that consistently delivers measurable value to organizations. The envisioning process establishes a connection between business goals and outcomes, identifies key metrics, and enables prioritization of cloud initiatives. The working backwards process translates this into a customer-facing narrative, allowing for validation of the vision with key stakeholders before development commences. The outcome is a clear linkage between enabling technologies, cloud initiatives, and stakeholder approval, focusing on the most critical business outcomes and success measures. Ideally, these initiatives should be developed iteratively and in collaboration with key stakeholders. Aligning Stakeholders to Overcome Blockers Once a shared vision is established, it is crucial to create a backlog of tasks, using Agile terminology such as epics and stories. The AWS CAF Align phase emphasizes the identification of capability gaps across six perspectives:
This phase also highlights cross-organizational dependencies and surfaces stakeholder concerns and challenges. Building upon the output of the envisioning process, the CAF Align phase develops a collaborative and practical action plan to facilitate the kickstart of a COM that aligns with key initiatives. This approach focuses on identifying blockers and addressing concerns from six groups of stakeholders. Each perspective encompasses a set of defined capabilities that are significantly impacted by cloud adoption. Through the CAF alignment approach, customers can understand and plan for the impact of cloud on various capabilities, not just the technological challenges. This framework helps customers recognize these changes as common and well-understood while developing a prescriptive action plan to address concerns and remove barriers to cloud adoption. Step 2: Re-envision the World as ProductsIn many organizations, the systems that support their business operations are often complex and tangled, developed over time without a clear structure. Even Amazon faced this challenge in the past, with a large, Java-based ecommerce application supporting its business. To transition to a product model that enables broader adoption and reuse of functionality beyond retail, a reimagining of individual products was necessary. Here are some examples: Identifying Individual Products To facilitate the transition, it was essential to identify the individual products that would make up the new architecture. This process involved rethinking the functionalities and components that would serve as the building blocks for the future architecture. It's important to note that this is not the same as refactoring the existing architecture. Refactoring can only occur once there is clarity on the components that will constitute the future architecture. Transitioning to a Product-Focused Approach for the Cloud Platform For the cloud platform, the shift involves moving away from an alignment centered around systems and technology. Instead, the focus is on creating collections of products, services, and technologies grouped together to form a cohesive product. This product-centric approach aligns with the four-point definition highlighted earlier in this document. Here are examples of cloud products, which may include a combination of AWS and non-AWS products and services:
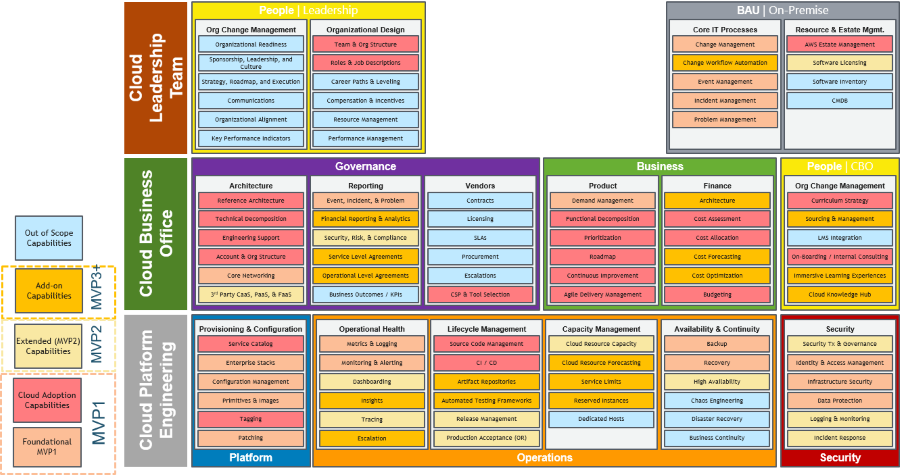
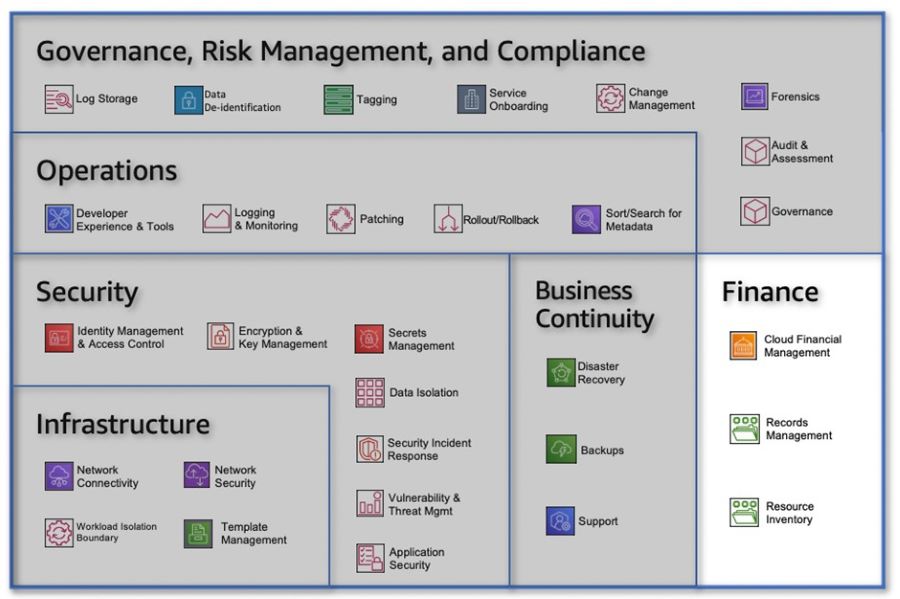
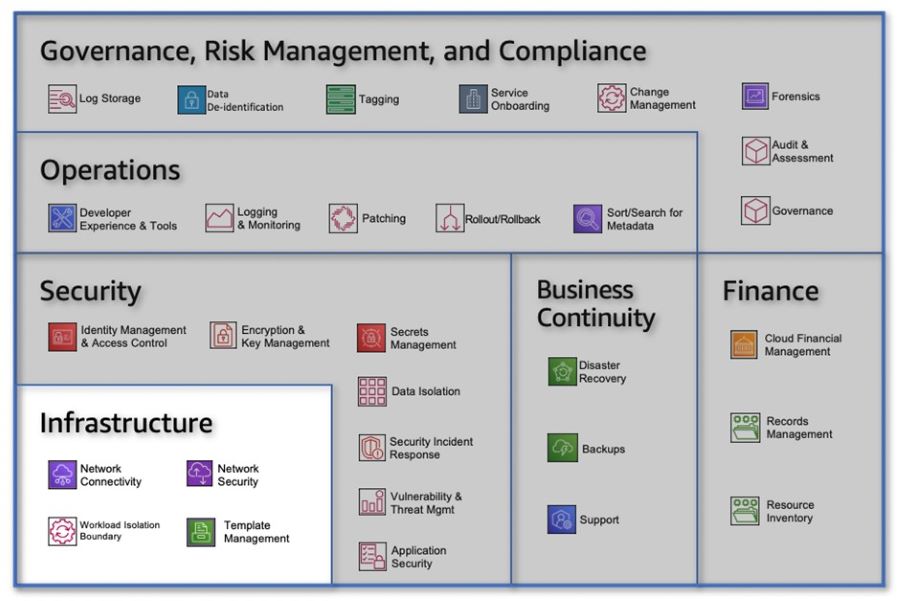
By organizing functionalities into distinct products, organizations can better manage and leverage their cloud platform. Each product represents a self-contained unit that can be independently developed, deployed, and maintained. This approach fosters modularity, scalability, and reusability, enabling organizations to derive maximum value from their cloud investments. It's worth emphasizing that the shift towards a product-focused approach requires a change in mindset and organizational structure. Teams need to align around products rather than systems and technologies, fostering collaboration and ownership within each product team. This shift allows for better customer-centricity, as teams can dedicate their efforts to delivering exceptional products and experiences that meet customer needs. By adopting a product-centric approach for the cloud platform, organizations can unlock the benefits of modularity, scalability, and reusability, driving innovation and delivering value to customers. Step 3: Organize the Teams around ProductsOnce a set of cloud products has been identified, the next step is to organize teams around the ownership and accountability of those products. A successful cloud operating model (COM) ensures that all components, including people, processes, and tools, are aligned to support each other effectively. As customer needs evolve over time, it is crucial to continuously evolve and meet their expectations. Clear product ownership is the key to achieving this. Formation of a Cloud Center of Excellence (CCoE) To establish effective product ownership, it is recommended to form a Cloud Center of Excellence (CCoE), consisting of two functional domains: Cloud Business Office (CBO) and Cloud Platform Engineering (CPE). The CBO focuses on aligning the CEE's products and services with the needs of enterprise customers and leadership. It takes charge of business governance and people enablement aspects of cloud adoption. Figure 3: CBO capabilities CBO Capabilities The CBO's responsibilities include:
CPE: Foundational Structure for the CBO Underpinning the CBO is Cloud Platform Engineering (CPE), which is responsible for codifying the differences between stock AWS service configurations and enterprise standards applicable within the organization. The CPE's role is to package and continuously improve the cloud platform as a set of self-service deployable products for customers and consumers. Figure 4 below, illustrates this structure. Figure 4: Cloud platform engineering capabilities Cloud Platform Engineering Capabilities The CPE teams have the following responsibilities:
By organizing teams around products and establishing clear ownership and accountability, organizations can effectively deliver cloud products and services. The CBO and CPE domains of the CEE play critical roles in aligning with customer needs, driving business outcomes, and ensuring the efficient deployment and operation of cloud solutions. Automation within the CPE further enhances resiliency, availability, and overall product quality. Step 4: Bring the Work to the TeamsInstead of building a comprehensive Cloud Enablement Engine (CEE) to support the entire business all at once, we recommend taking an incremental approach. Think big, but start small. This approach allows teams and customers to build and learn iteratively as they scale their adoption of cloud solutions. The Cloud Foundation Team The initial product team in the CEE is known as the Cloud Foundation Team. It should be cross-functional and encompass all the necessary roles and capabilities that will eventually expand into a full-fledged CEE. When staffing a product team, it is important to consider and balance four key concerns or perspectives:
Scaling the Cloud Foundation Team As cloud adoption expands, the Cloud Foundation Team must grow and scale to keep pace with the AWS customer journey. Although each customer journey is unique, successful cloud adopters often follow a pattern of subdivision and specialization. Typically, the initial CEE is divided into four product teams: one for the Cloud Business Office (CBO) and three for the Cloud Platform Engineering (CPE). In larger organizations, this subdivision and specialization process continues based on the backlog of work. Key Roles in the Cloud Foundation Team The cloud foundation team requires the following key roles:
Additional Roles in the Cloud Foundation Team Other roles that are typically added to the cloud foundation team, though they may be part-time, include:
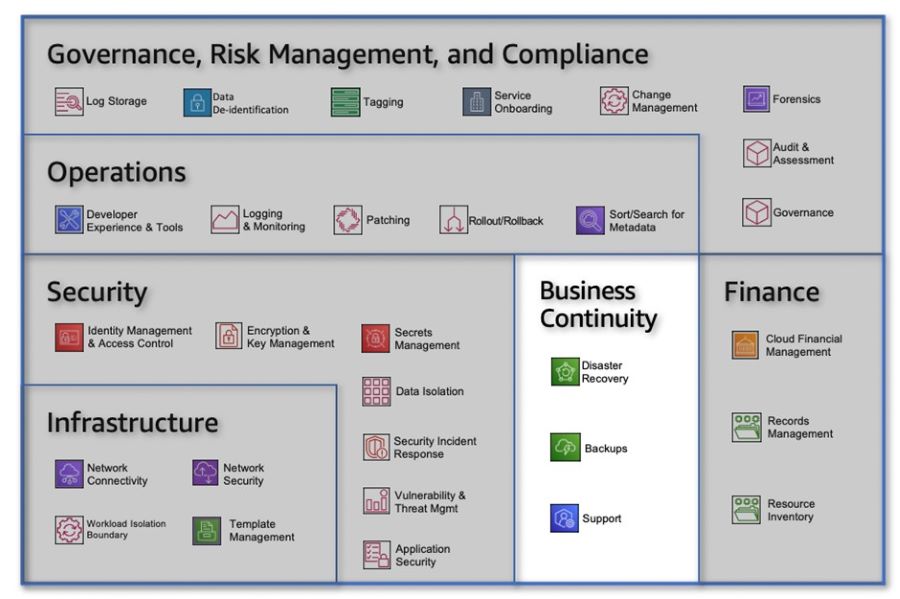
By bringing the work to the teams and establishing the Cloud Foundation Team, organizations can effectively start their cloud journey. These teams, with their defined roles and responsibilities, provide the necessary foundation for driving successful cloud adoption and delivering business outcomes in a structured and efficient manner. Step 5: Reduce Risk through Iteration and Automation Implementing an effective operating model is an ongoing process that requires continuous improvement through measurement and testing. All product teams share the responsibility of establishing measures to ensure they deliver the expected outcomes and operate within acceptable limits. In this model, product owners are accountable for measuring not only their product's performance but also the services on which their product relies. Transparent metrics and measures provided and consumed by different product teams enable informed decision-making. Embedding Testing and Automation To maintain the functionality of the operating model when introducing new products, it is crucial to incorporate constant, automated, and standardized testing into the development process. This testing serves two important purposes:
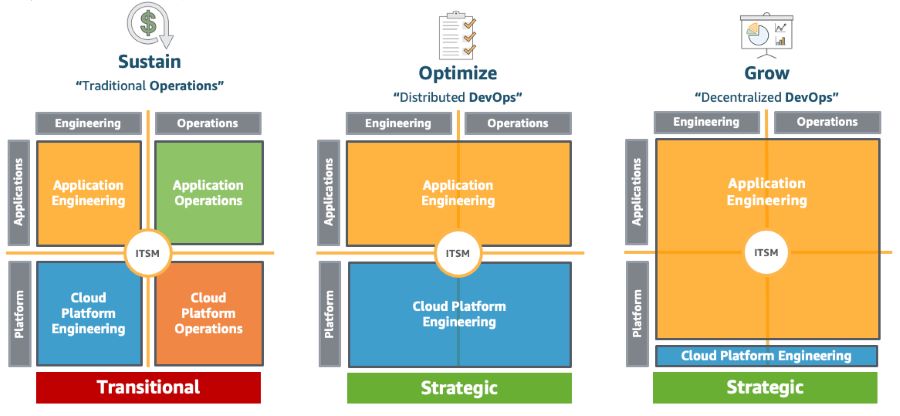
By integrating robust testing practices and automation into the development and deployment of new products, organizations can significantly reduce risks associated with failures and ensure the smooth functioning of the operating model. Regular testing and simulation provide valuable insights that contribute to the continuous improvement and optimization of the cloud environment. Step 6: Own Your Own LifecycleThe cloud presents opportunities to address accumulated workarounds and neglected IT systems by adopting a proactive approach. However, organizations must be cautious not to fall into the trap of pursuing perfection at the expense of practicality. Successful adopters take two key actions to help ensure they own their own lifecycle and deliver meaningful benefits. First, they align the operating model delivery approach to the strategic value of the workload and second, successful COMs and CEEs establish a clear roadmap of delivering capabilities and processes that align and underpin the ability to establish production operations in an MVP and iterative approach. Operating Model Options When it comes to the operating model, it's important to acknowledge that not everyone will immediately embrace a DevOps approach. My engagements with customers have revealed three broad operating models, as shown in Figure 5 below. Figure 5: Modernizing IT Sustain This model follows a traditional operations approach, similar to the activity-based models found in most organizations. It is best suited for lift-and-shift workloads that require minimal operational changes due to their limited lifespan or infrequent changes. Optimize In this model, application engineering teams take on the responsibility for both application development and operations. This resembles a DevOps approach for application teams, where they own the complete lifecycle of their applications. Platform teams, represented by the Cloud Platform Engineering (CPE), provide codified enterprise standards and governance to enable application teams to iterate quickly without burdening them with deep implementation details. Grow This model is adopted by teams seeking to leverage the latest AWS services and push technological boundaries. Application engineering teams take ownership of their applications while being empowered to build platform capabilities that are not yet standardized by the CPE. The CPE ensures that application teams adhere to enterprise-wide security, financial, and operational guidelines. It's important to note that these models are not indicative of maturity levels and can coexist within an organization. However, there is often a natural progression towards the "optimize" model, with "sustain" workloads being phased out and platform services used by "grow" workloads eventually becoming new enterprise standards. Delivery Roadmap Organizations already have established operational processes and procedures for IT delivery and change management, which may align with frameworks like ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library). AWS has developed an operational integration domain-based blueprint model to support the establishment of a Cloud Operating Model (COM) and Cloud Enablement Engine (CEE). The AWS Operations Domains framework represents a best-practice-based approach to transform existing ITIL-based operating models into cloud-adapted architectures. Figure 6: AWS Operational Domain Model The AWS Operational Domain model covers various operational aspects and aligns with the responsibilities of the CEE. It continuously evolves through continuous improvement efforts and serves as a foundation for operational processes required by most customers. However, organizations may need to consider additional operational processes unique to their specific needs or specialized industries. This domain model facilitates communication and provides a roadmap for the CEE's operational capabilities across Minimum Viable Product (MVP) cycles. It helps the CEE take ownership and establish its operating model roadmap, aligning with industry standards like ITIL while adapting to the specific requirements of cloud platforms. Owning your own lifecycle in the cloud requires aligning the delivery approach with strategic value and establishing a clear roadmap for capabilities and processes. By understanding and implementing the appropriate operating model, organizations can optimize their cloud adoption journey while considering the unique needs of different workloads. Figure 6: The operational capability roadmap Additionally, leveraging frameworks such as ITIL and AWS operational domains provides a structured approach for transforming existing operating models into cloud-enabled architectures. With a well-defined roadmap and continuous improvement efforts, organizations can navigate the cloud landscape and derive maximum value from their cloud investments. Next StepsTo embark on a successful transformation, organizations must adopt an iterative and incremental approach to improving their operating model and embrace a product-based mindset in IT delivery. This section highlights the best practices covered in this guide for establishing a cloud operating model.
By following these guidelines, you can establish a strong foundation for your cloud operating model. This approach can serve as a blueprint that can be emulated and scaled to other parts of your organization, enabling a successful cloud transformation journey. Embrace the iterative and incremental mindset, prioritize clear objectives, and engage your teams in continuous learning and improvement to achieve long-term success. ConclusionEstablishing a Cloud Operating Model (COM) brings significant benefits to organizations. Beyond cost savings, it leads to reduced downtime, accelerated delivery of services, increased productivity, and improved staff morale. To avoid common pitfalls such as unexpected costs, slow adoption, outages, and security breaches, organizations should proactively develop a new operating model. Organizations that proactively establish a COM can reap numerous benefits beyond cost savings. By following the six-step approach outlined in this whitepaper, cloud adoption leaders can develop a successful COM that meets business needs and overcomes common pitfalls. Embrace the opportunity to transform your organization and unlock the full potential of the cloud.
0 Comments
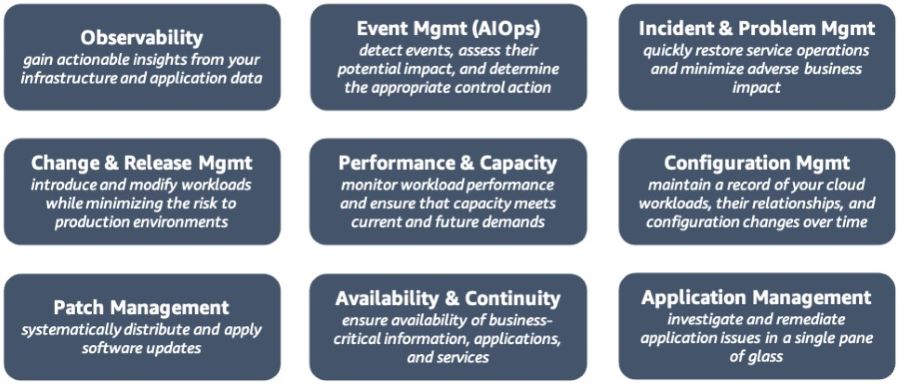
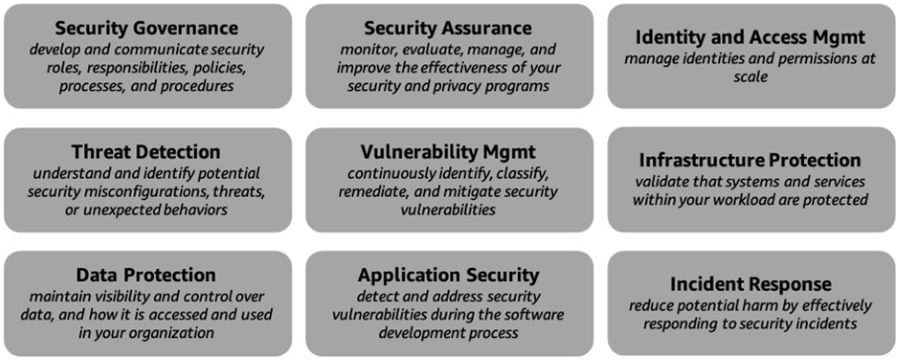
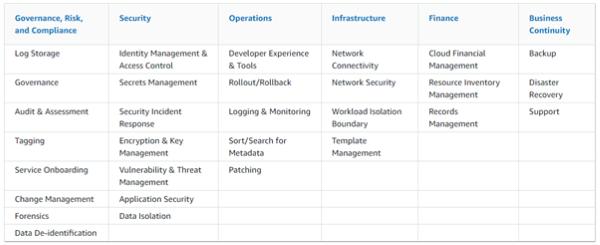
Throughout this series, we have explored the various perspectives of AWS CAF, providing valuable insights and practical guidance to help organizations successfully embrace the power of the cloud. The Operations Perspective within AWS CAF focuses on optimizing the health, availability, and performance of cloud services, aligned with the specific needs and goals of your organization. This perspective encompasses a range of capabilities outlined below, and involves various stakeholders such as infrastructure and operations leaders, site reliability engineers, and information technology service managers. Figure 1: AWS CAF Operations perspective capabilities Observability Observability is a critical capability that enables organizations to derive valuable insights from their infrastructure and application data. Operating at cloud speed and scale requires the ability to proactively identify issues before they disrupt the customer experience. To achieve this, it is essential to develop comprehensive telemetry comprising logs, metrics, and traces that provide a deep understanding of the internal state and health of workloads. Monitoring application endpoints and assessing their impact on end users is crucial for maintaining optimal performance. By generating alerts when measurements exceed predefined thresholds, organizations can quickly address potential problems. Synthetic monitoring, which involves using configurable scripts scheduled to run at regular intervals, allows the creation of canaries to monitor endpoints and APIs effectively. Implementing traces provides visibility into the journey of requests throughout the entire application, enabling the identification of bottlenecks and performance issues. By leveraging metrics and logs, insights can be gained into the utilization of resources, servers, databases, and networks. Real-time analysis of time series data helps in understanding the causes behind performance impacts, facilitating prompt remediation. To consolidate observability data, organizations can centralize it in a single dashboard, providing a unified view of critical information about workloads and their performance. This centralized view enhances situational awareness and empowers teams to make informed decisions and take timely actions to optimize operations and ensure a seamless customer experience in the cloud environment. Event Management (AIOps) Event management, with the integration of Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations (AIOps), plays a crucial role in effectively detecting events, assessing their potential impact, and determining appropriate control actions. In order to optimize incident detection and response times, it is important to filter out irrelevant noise and focus on priority events that require immediate attention. Predicting impending resource exhaustion and automatically generating alerts and incidents enable proactive monitoring and mitigation of potential issues before they escalate. Furthermore, identifying likely causes and remediation actions helps in swiftly resolving incidents and minimizing their impact on operations. Establishing an event store pattern and harnessing the power of machine learning through AIOps allow for automated event correlation, anomaly detection, and causality determination. This enables organizations to efficiently analyze large volumes of event data and identify patterns or anomalies that might indicate underlying issues. Integration with cloud services and third-party tools, including incident management systems and processes, enhances the overall event management capabilities. By automating responses to events, organizations can reduce errors that may result from manual processes and ensure consistent and prompt actions, thereby improving incident response efficiency and effectiveness. Incident and Problem Management Incident and problem management aims to swiftly restore service operations and minimize adverse impacts on business operations. The adoption of cloud technology enables organizations to automate response processes for service issues and application health concerns, resulting in improved service uptime. As organizations transition to a more distributed operating model, it becomes essential to streamline interactions between relevant teams, tools, and processes. This streamlining facilitates the prompt resolution of critical and complex incidents, ensuring minimal disruption to operations. Within runbooks, it is important to define escalation paths that outline triggers and procedures for escalating incidents to appropriate personnel. Conducting incident response gamedays and incorporating lessons learned into runbooks allows organizations to enhance their incident management capabilities. By identifying incident patterns, organizations can determine underlying problems and implement corrective measures effectively. Leveraging chatbots and collaboration tools facilitates seamless communication and coordination among operations teams, tools, and workflows. Furthermore, adopting blameless post-incident analyses enables organizations to identify contributing factors to incidents without assigning blame. This approach encourages a focus on learning and improvement, leading to the development of targeted action plans to prevent similar incidents in the future. Change and Release Management Change and release management involves the introduction and modification of workloads while mitigating risks to production environments. Traditional release management is known for its complexity, slow deployment speed, and challenges associated with rollbacks. However, with the adoption of cloud technology, organizations can leverage Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) techniques to facilitate rapid release management and rollbacks. To align with the agility of the cloud, it is crucial to establish change processes that incorporate automated approval workflows. This enables seamless and efficient handling of changes. Deployment management systems should be utilized to effectively track and implement these changes. By adopting a strategy of frequent, small, and reversible changes, the scope of each modification is minimized, reducing potential disruptions. Thoroughly testing and validating changes at every stage of the lifecycle is essential to minimize the risks and impacts of failed deployments. Automating the rollback process to a previously known stable state is crucial in cases where desired outcomes are not achieved. This automated rollback mechanism reduces recovery time and minimizes errors that can occur with manual processes. Overall, embracing cloud technology and implementing effective change and release management practices enable organizations to introduce and modify workloads with reduced risk to production environments, while benefiting from the agility and efficiency of CI/CD techniques. Performance and Capacity Management Performance and capacity management involves monitoring the performance of workloads and ensuring that the available capacity meets both current and future demands. While the cloud offers virtually unlimited capacity, various factors such as service quotas, capacity reservations, and resource constraints can limit the actual capacity of your workloads. It is crucial to understand and effectively manage these capacity constraints. To achieve this, it is important to identify key stakeholders and reach a consensus on the objectives, scope, goals, and metrics of performance and capacity management. Collecting and processing performance data on a regular basis is necessary to track progress and report on performance against established targets. Periodically evaluating new technologies can help identify opportunities for performance improvements and recommend necessary changes to goals and metrics accordingly. Monitoring the utilization of workloads is essential for creating baselines that serve as reference points for future comparisons. By establishing thresholds, you can identify when it's necessary to expand capacity to meet increasing demands. Analyzing demand patterns over time is crucial to ensure that the capacity aligns with seasonal trends and fluctuating operating conditions. In summary, effective performance and capacity management require continuous monitoring of workload performance, understanding and addressing capacity constraints, engaging stakeholders, collecting performance data, and making informed decisions based on analysis to optimize performance and ensure sufficient capacity to meet evolving demands. Configuration Management When it comes to configuration management, it's essential to maintain accurate and complete records of all your cloud workloads, their relationships, and any changes made to their configurations over time. If not properly managed, the dynamic and virtual nature of cloud resource provisioning can lead to what's known as configuration drift, where things get out of sync. To stay on top of it, it's important to establish a tagging system that overlays your business attributes onto your cloud usage, allowing you to organize your resources based on technical, business, and security factors. Make sure to specify mandatory tags and enforce compliance through policies to ensure consistency. Leveraging infrastructure as code (IaC) and configuration management tools will simplify resource provisioning and lifecycle management. Lastly, establish configuration baselines and keep them up to date through version control, so you always have a solid reference point to work from. Patch Management When it comes to patch management, it's important to have a systematic approach in place to ensure the timely distribution and application of software updates. These updates address security vulnerabilities, fix bugs, and introduce new features to keep your systems running smoothly. By following a structured patch management process, you can take advantage of the latest updates while minimizing any risks to your production environments. To implement effective patch management, it's crucial to apply important updates during designated maintenance windows and prioritize critical security updates for immediate action. Providing advance notice to users about upcoming updates and giving them the option to defer patches when alternative mitigations are available can help maintain a smooth transition. Before rolling out patches to your production environment, it's advisable to update your machine images and thoroughly test the patches to ensure compatibility and stability. Considering separate maintenance windows for each Availability Zone (AZ) and environment will help ensure uninterrupted availability during the patching process. Regularly reviewing patching compliance and promptly notifying non-compliant teams to apply the required updates will help keep your systems secure and up to date. By staying vigilant in your patch management efforts, you can effectively protect your systems while keeping them running smoothly. Availability and Continuity Management In terms of ensuring the availability of business-critical information, applications, and services, availability and continuity management plays a vital role. To build robust cloud-enabled backup solutions, it's important to carefully assess your existing technology investments, recovery objectives, and available resources. By ensuring timely restoration after disasters and security events, you can maintain system availability and business continuity. One crucial aspect is to establish a well-defined schedule for backing up your data and documentation. This ensures that you have the necessary safeguards in place to protect your valuable assets. To enhance your overall preparedness, it's recommended to develop a disaster recovery plan as part of your broader business continuity strategy. This involves identifying potential threats, assessing risks, evaluating the impact, and estimating the costs associated with different disaster scenarios for each workload. By specifying Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPOs) accordingly, you can align your recovery efforts with business needs. Implementing a disaster recovery strategy that leverages multi-AZ or multi-Region architecture can provide added resilience and minimize potential disruptions. Additionally, considering the use of chaos engineering, which involves conducting controlled experiments to improve resiliency and performance, can further enhance your overall system robustness. It's crucial to regularly review and test your plans, ensuring they remain up to date and effective. By incorporating lessons learned from previous experiences, you can refine your approach and make any necessary adjustments to strengthen your availability and continuity management practices. Application Management When it comes to application management, the ability to investigate and resolve application issues from a single interface is crucial. By consolidating application data into a unified management console, you can simplify operational oversight and expedite the remediation process. This eliminates the need to constantly switch between various management tools, streamlining the workflow. To enhance efficiency further, it's important to integrate your application management with other operational and management systems. This includes systems like application portfolio management and Configuration Management Database (CMDB). By automating the discovery of application components and resources, you can gain a comprehensive view of your application landscape. Consolidating all relevant data into a single management console provides a holistic perspective. This approach should encompass both software components and infrastructure resources, encompassing different environments such as development, staging, and production. By clearly delineating these environments, you can better understand the context in which application issues occur. To facilitate quicker and more consistent resolution of operational issues, consider automating your runbooks. By automating routine operational tasks and predefined procedures, you can streamline the response to incidents and reduce manual effort. In summary, by leveraging a single management console, integrating with other operational systems, and automating runbooks, you can effectively manage your applications, investigate issues efficiently, and expedite the remediation process. ConclusionIn this final articles in our series on the AWS Cloud Adoption Framework (AWS CAF), we have explored the Operations Perspective and its critical role in driving the success of cloud adoption initiatives, examining the key capabilities and best practices that empower organizations to optimize the health, availability, and performance of their cloud services within the AWS ecosystem. By embracing the Operations Perspective, organizations can leverage automation, real-time insights, and robust incident response mechanisms to maintain the reliability, security, and performance of their cloud workloads. This holistic approach to operations fosters agility, reduces downtime, and enhances the overall efficiency of cloud environments. As we conclude this series on AWS CAF, it is essential to reflect on the wealth of knowledge we have gained throughout the various perspectives. We have explored the Business, People, Governance, Platform, Security, and Operations Perspectives, collectively providing a comprehensive framework for successful cloud adoption journeys. By adopting AWS CAF as a guiding principle, organizations can align their strategies, optimize resources, and achieve their desired business outcomes in the cloud. The series has equipped cloud architects, IT professionals, and decision-makers with practical insights and actionable steps to navigate the complexities of cloud adoption and unlock the full potential of AWS services. As technology continues to evolve, the AWS Cloud Adoption Framework remains a valuable resource for organizations embarking on their cloud transformation journeys. By leveraging the framework's principles and applying the knowledge gained from this series, businesses can confidently navigate the ever-changing landscape of cloud computing, ensuring long-term success and innovation. I hope that this series has provided you with the necessary guidance and inspiration to embrace the AWS Cloud Adoption Framework and embark on a transformative cloud journey. A focus on security is paramount to establish a robust foundation that safeguards your organization's assets and mitigates risks in the cloud. In this article, we will explore the key capabilities that will help you strengthen your security posture and respond effectively to security threats and incidents. It comprises nine capabilities shown in the figure below. Common stakeholders include CISO, CCO, internal audit leaders, and security architects and engineers. Figure 1: AWS CAF Security perspective capabilities Security Governance Security governance is a vital aspect of establishing a robust security program. It involves developing, maintaining, and effectively communicating security roles, responsibilities, accountabilities, policies, processes, and procedures. By ensuring clear lines of accountability, you can enhance the effectiveness of your security efforts. In the context of cloud security, it is crucial to understand your responsibility for safeguarding data and workloads. This includes conducting an inventory of relevant stakeholders, assets, and information exchanges. Additionally, you need to identify the applicable laws, rules, regulations, and industry standards/frameworks that govern your organization. Performing regular risk assessments enables you to evaluate the likelihood and impact of identified risks and vulnerabilities specific to your organization. By allocating sufficient resources to identified security roles and responsibilities, you can strengthen your security posture. It is essential to develop security policies, processes, procedures, and controls aligned with your compliance requirements and organizational risk tolerance. Continuously updating them based on evolving risks and requirements ensures that your security measures remain effective. By adhering to these practices, you can establish a solid foundation for security in the cloud, prioritize your security efforts, and provide ongoing direction and advice to your teams, enabling them to operate with greater agility and efficiency. Security Assurance Security assurance is a continuous process of monitoring, evaluating, managing, and enhancing the effectiveness of your security and privacy programs. It is essential to instill trust and confidence in your organization and the customers you serve, assuring them that the implemented controls enable you to meet regulatory requirements and effectively manage security and privacy risks aligned with your business objectives and risk tolerance. To achieve security assurance, it is important to document controls within a comprehensive control framework. This framework should establish demonstrable security and privacy controls that align with your objectives. It is beneficial to review audit reports, compliance certifications, or attestations obtained by your cloud vendor. This helps you gain insights into the controls they have implemented, how these controls have been validated, and the effectiveness of controls within your extended IT environment. Continuously monitoring and evaluating your environment is crucial to verify the operational effectiveness of your controls and demonstrate compliance with regulations and industry standards. Regularly reviewing security policies, processes, procedures, controls, and records is necessary to ensure they remain up to date and aligned with your security objectives. Conducting interviews with key personnel as required further enhances your understanding of the security landscape and aids in identifying any areas that require improvement. Identity and Access Management Identity and access management (IAM) involves the management of identities and permissions at a large scale. In AWS, you have the flexibility to create identities within the platform or connect to your existing identity source. By granting users the appropriate permissions, they can securely sign-in, access, provision, and orchestrate AWS resources and integrated applications. Effective IAM practices play a vital role in ensuring that the correct individuals and machines have access to the right resources, under the appropriate conditions. The AWS Well-Architected Framework provides valuable guidance on managing identities by outlining relevant concepts, design principles, and architectural best practices. These include leveraging a centralized identity provider, utilizing user groups and attributes for precise access control at scale, and implementing robust sign-in mechanisms like multi-factor authentication (MFA). To govern access for both human and machine identities to AWS and your workloads, it is essential to define permissions for specific service actions, resources, and conditions. Adhering to the principle of least privilege (PoLP), setting permissions boundaries, and utilizing service control policies enable the appropriate entities to access the necessary resources as your environment and user base expand. Granting permissions based on attributes (Attribute-Based Access Control or ABAC) allows your policies to scale effectively. Continuously validating your policies ensures that they provide the necessary protection in alignment with your security requirements. Threat Detection Threat detection is crucial in understanding and identifying potential security misconfigurations, threats, or unexpected behaviors. By gaining a deeper comprehension of security threats, you can prioritize the implementation of protective controls. Effective threat detection enables prompt response to threats and facilitates learning from security incidents. It is essential to establish consensus on tactical, operational, and strategic intelligence goals, as well as an overall methodology. This involves mining relevant data sources, processing and analyzing data, and disseminating and operationalizing valuable insights. To ensure comprehensive coverage, deploy monitoring mechanisms ubiquitously throughout your environment to collect essential information. Additionally, deploy monitoring at ad hoc locations to track specific types of transactions as needed. By correlating monitoring data from multiple event sources such as network traffic, operating systems, applications, databases, and endpoint devices, you can establish a robust security posture and enhance visibility into potential threats. Consider leveraging deception technology, such as honeypots, as a strategic approach to gain insights into unauthorized user behavior patterns and enhance your overall threat detection capabilities. Vulnerability Management Vulnerability management involves the ongoing process of identifying, categorizing, remediating, and mitigating security vulnerabilities. It's important to note that vulnerabilities can emerge not only from changes to existing systems but also from the introduction of new systems. To safeguard against new threats, it's crucial to conduct regular vulnerability scans. By employing vulnerability scanners and endpoint agents, you can associate systems with known vulnerabilities and take appropriate measures. Prioritizing remediation actions based on the level of vulnerability risk is essential. This allows you to allocate resources effectively and address the most critical vulnerabilities first. After applying the necessary remediation actions, it is important to report the progress to relevant stakeholders to ensure transparency and accountability. To enhance your vulnerability management practices, consider leveraging techniques such as red teaming and penetration testing. These approaches help identify vulnerabilities in your system architecture by simulating real-world attack scenarios. However, it's important to seek prior authorization from your cloud provider when performing such activities. This ensures compliance with any necessary guidelines and regulations. Infrastructure Protection Infrastructure protection involves validating that the systems and services within your workload are safeguarded against unintended and unauthorized access, as well as potential vulnerabilities. By effectively protecting your infrastructure from such risks, you can significantly enhance your security posture in the cloud. One recommended approach is to implement defense in depth, which involves layering a series of defensive mechanisms to protect your data and systems. To implement infrastructure protection measures, you can create network layers and segregate workloads with no need for internet access into private subnets. Utilizing security groups, network access control lists, and network firewalls enables you to control and regulate traffic flow. Applying the Zero Trust principle ensures that access to your systems and data is granted based on strict verification, taking into account their value and sensitivity. Leveraging virtual private cloud (VPC) endpoints allows for private connections to cloud resources, ensuring secure communication. It is important to inspect and filter traffic at each layer of your infrastructure, such as employing web application firewalls and network firewalls. Additionally, using hardened operating system images and physically securing any on-premises and edge infrastructure in a hybrid cloud environment further strengthens your protection measures. Data Protection Protecting your data from unintended and unauthorized access, as well as potential vulnerabilities, is a crucial objective of your security program. To establish appropriate protection and retention controls, it is important to classify your data based on its criticality and sensitivity, such as personally identifiable information. Define data protection controls and establish lifecycle management policies to ensure the secure handling of data. Encrypting all data at rest and in transit, and storing sensitive data in separate accounts, adds an extra layer of protection. Leveraging machine learning capabilities can aid in automatically discovering, classifying, and safeguarding sensitive data. By maintaining control over data access and usage, you can minimize the risk of data breaches and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. Application Security Application security plays a crucial role in identifying and resolving security vulnerabilities throughout the software development process. By proactively detecting and addressing security flaws during the coding phase, you can significantly reduce the time, effort, and expenses associated with fixing issues later on. This proactive approach instills confidence in the security posture of your application as it moves towards production. To protect against emerging threats, it is important to conduct regular scans and apply patches to address vulnerabilities in your code and dependencies. By automating security-related tasks across your development and operations processes and utilizing tools, you can minimize the reliance on manual intervention and streamline the security workflow. Employing static code analysis tools helps identify and mitigate common security issues, further fortifying the overall security of your applications. By prioritizing application security and integrating it into your development lifecycle, you can establish a robust defense against potential security risks and ensure the integrity and reliability of your software systems. Incident Response In the realm of incident response, it is crucial to swiftly and effectively address security incidents to minimize potential harm. By responding promptly, efficiently, and consistently to such incidents, you can significantly mitigate their impact. To ensure readiness, it is important to educate your security operations and incident response teams about cloud technologies and their intended use within your organization. Creating runbooks and establishing an incident response library can provide valuable guidance and resources for your teams. It is also essential to involve key stakeholders, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of the potential organizational impact resulting from your incident response choices. To enhance preparedness, it is beneficial to simulate security events and conduct tabletop exercises and game days to practice your incident response procedures. Through these simulations, you can identify areas for improvement, enhance the scalability of your response posture, and reduce both the time to value and overall risk. Moreover, conducting post-incident analyses using standardized mechanisms can enable you to learn from security incidents and effectively identify and address root causes. By prioritizing incident response and continually refining your approach, you can bolster your organization's ability to effectively handle security incidents, minimize their consequences, and foster a proactive security culture. SummaryPart 6 of our series on the AWS Cloud Adoption Framework has provided valuable insights into the Security Perspective. We have explored nine critical capabilities that enable you to establish a strong security foundation, including security governance, threat detection, vulnerability management, and data protection. By implementing these capabilities, you can effectively manage security risks, protect your data, and respond efficiently to security incidents. As we reach the final installment of our series, we now shift our focus to the Operations Perspective. Join us in Part 7 as we explore the key capabilities that will enable you to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and maximize the value of your cloud investment. Get ready to unlock the full potential of your cloud environment in our last article of the series.
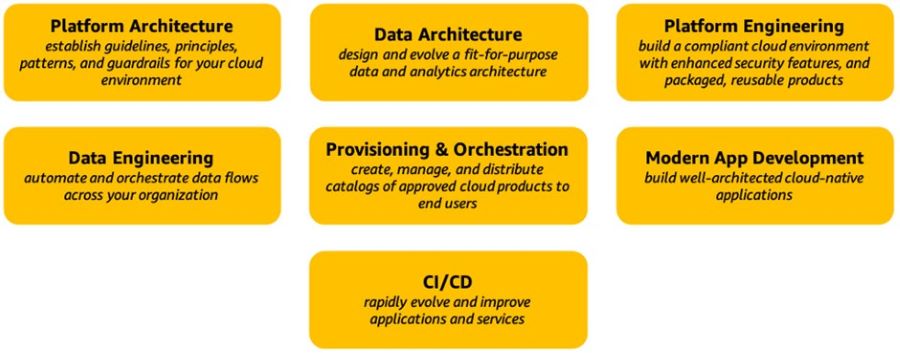
The Platform Perspective encompasses seven essential capabilities that are vital for success as shown in the figure below. Figure 1: AWS CAF Platform perspective capabilities Platform Architecture
Data Architecture
Platform Engineering
Data Engineering
Provisioning and Orchestration
Modern Application Development
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD)
SummaryThe Platform Perspective is a crucial framework for accelerating the delivery of cloud workloads and achieving success in your cloud initiatives. By establishing guidelines, principles, and guardrails for your cloud environment, you can create a well-architected foundation that accelerates implementation, reduces risk, and drives cloud adoption. With the Platform Perspective as your guide, you can navigate the complexities of infrastructure and applications, harnessing the power of an enterprise-grade, scalable, and hybrid cloud environment. By embracing these capabilities, you will be well-equipped to meet the demands of today's dynamic business landscape and drive successful outcomes in your cloud initiatives. In Part 6, we will explore the crucial elements and best practices for securing your cloud workloads, protecting your data, and mitigating risks. From identity and access management to network security, data protection, and compliance, the Security Perspective plays a pivotal role in ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of your cloud environment. Governance plays a vital role in providing control and oversight to ensure that cloud adoption aligns with strategic objectives and delivers value to the organization. Indeed, when it comes to cloud transformation, the governance perspective plays a vital role in ensuring the success of your initiatives while minimizing risks. This perspective focuses on control and oversight, allowing you to maximize the benefits for your organization. Within the governance perspective, there are seven key capabilities that are crucial to consider, as depicted in the figure below. Common stakeholders involved in this perspective include the chief transformation officer, CIO, CTO, CFO, CDO, and CRO. Figure 1: AWS CAF Governance perspective capabilities Program and Project Management Delivering complex cross-functional cloud transformation initiatives requires careful coordination, especially in organizations with more traditional structures. Program management becomes especially critical, as it helps align multiple initiatives to optimize costs, schedules, efforts, and benefits. It is important to regularly validate your roadmap with business sponsors, escalating any issues to senior leadership to ensure accountability and transparency. An agile approach is recommended, allowing you to learn from experience and adapt as you progress through your transformation journey. Benefits Management The success of your cloud transformation relies on the realization and sustenance of business benefits. Clearly identifying desired benefits from the outset enables you to prioritize your investments and track progress over time. It is essential to establish metrics, quantify desired benefits, and communicate them to relevant stakeholders. Align the timing and life-span of benefits with your strategic goals and incorporate them into a benefits realization roadmap. Regularly measuring realized benefits and evaluating progress against the roadmap will help you make necessary adjustments. Risk Management Cloud adoption presents opportunities to reduce operational and business risks. It is crucial to identify and quantify risks related to infrastructure availability, reliability, performance, security, reputation, business continuity, and market responsiveness. Understanding how cloud can help mitigate these risks and continuously identifying and managing them within your agile cadence is key. By leveraging cloud capabilities, you can minimize upfront infrastructure expenditures, mitigate procurement schedule risks, and easily provision and deprovision resources as needed. Cloud Financial Management Combining the agility of cloud with financial accountability is essential for effective cloud financial management. Clarifying financial roles and responsibilities pertaining to cloud and ensuring a shared understanding of cloud costs among key stakeholders are critical steps. Adopting a more dynamic forecasting and budgeting process allows for better cost optimization. Aligning account structures and tagging strategies with your organization's mapping to the cloud provides a granular view of consumption patterns. Implementing guardrails to govern cloud usage, leveraging demand-based and time-based dynamic provisioning, and centralizing license management all contribute to optimizing cloud spend. Application Portfolio Management Managing and optimizing your application portfolio is crucial for supporting your business strategy. An accurate and complete application inventory enables you to identify opportunities for rationalization, migration, and modernization. Minimizing application sprawl, facilitating application lifecycle planning, and ensuring ongoing alignment with your cloud transformation strategy are key objectives. By starting with critical applications, mapping them to business capabilities and associated resources, and periodically enriching and validating application metadata, you can assess and maximize the value derived from your application investments. Data Governance Data is the foundation for business processes and analytics, and effective data governance ensures its accuracy, completeness, timeliness, and relevance. Defining key roles, specifying standards, and establishing data quality standards are crucial steps. Monitoring data quality, identifying and addressing root causes of data quality problems, and implementing data quality dashboards help maintain data integrity. Additionally, establishing data lifecycle policies, modeling relationships between reference data entities, and ensuring compliance contribute to effective data governance. Data Curation Data curation involves collecting, organizing, accessing, and enriching metadata to build a comprehensive inventory of data products in a Data Catalog. A Data Catalog facilitates data monetization and self-service analytics by helping data consumers quickly locate relevant data products and understand their context. By identifying lead curators, cataloging key data products, capturing metadata (including lineage), leveraging automation and standard ontologies, and considering crowdsourcing for data enrichment, you can enhance the value and usability of your data assets. SummaryThe Governance Perspective plays a vital role in effectively orchestrating cloud initiatives while ensuring maximum organizational benefits and mitigating risks. By leveraging the seven governance capabilities discussed in this article, organizations can establish control, optimize resources, and align their cloud transformation strategy with business objectives. Strong governance empowers stakeholders and promotes accountability, transparency, and informed decision-making. By delving deeper into each governance capability, organizations can further enhance their cloud governance practices and successfully navigate their transformation journey. Join us in Part 5 of our series as we take a closer look at the Platform Perspective and the core building blocks that form the foundation of cloud platforms, examining how they enable agility, scalability, and innovation.
As organizations embark on their cloud journeys, it becomes increasingly evident that success lies not only in adopting cutting-edge technologies but also in cultivating a supportive and adaptive culture that empowers employees and aligns with digital transformation aspirations. The People Perspective encompasses seven essential capabilities that contribute to this cultural evolution, organizational structure, leadership, and workforce development. People Perspective: Culture and ChangeThe People Perspective acts as a vital link between technology and business, expediting the cloud journey and enabling organizations to swiftly transition to a culture of continuous growth, learning, and embracing change as the new normal. This perspective encompasses seven key capabilities, as illustrated in the following diagram. Key stakeholders in this perspective include the CIO, COO, CTO, cloud director, and leaders across different functions and the enterprise. Figure 1: AWS CAF People Perspective Capabilities Culture Evolution
Transformational Leadership
Cloud Fluency
Workforce Transformation
Change Acceleration
Organization Design
Organizational Alignment
SummaryThe People Perspective is instrumental in driving successful cloud transformation by nurturing a culture of growth, learning, and change within organizations. By focusing on the key capabilities, organizations can create an environment that empowers their workforce and accelerates their cloud journey. In Part 3, we explored the importance of culture, leadership, workforce development, and organizational alignment. We highlighted the need to evolve organizational culture, strengthen leadership capabilities, build digital acumen, enable workforce transformation, accelerate change adoption, align organization design, and establish organizational alignment. These aspects are vital for organizations seeking to thrive in the cloud era. Join us in Part 4 as we explore the Process Perspective and discover how organizations can drive impactful changes that revolutionize their operations and drive business success in the cloud era. Now, let's dive deeper into the specific capabilities that comprise the Business Perspective: Strategy and Outcomes. Within this perspective, there are eight key capabilities that play a crucial role in aligning your cloud strategy with your long-term business goals. From strategy management and portfolio prioritization to innovation, product management, strategic partnerships, data monetization, business insights, and data science, each capability offers unique insights and strategies to maximize the value of your cloud investments. By understanding and effectively implementing these capabilities, organizations can gain a competitive edge, foster innovation, and transform their operations to thrive in today's dynamic business landscape. So, join us as we explore the Business Perspective: Strategy and Outcomes, and discover how these capabilities can empower your organization to achieve its digital transformation goals and drive measurable business success. Let's dive into the first capability within the Business Perspective The business perspective within the AWS Cloud Adoption Framework (AWS CAF) focuses on leveraging your cloud investments to accelerate your digital transformation ambitions and drive tangible business outcomes. This perspective comprises eight key capabilities that are essential for success. Common stakeholders include the CEO, CFO, COO, CIO, and CTO. Figure 1: AWS CAF Business perspective capabilities Strategy Management Harness the power of the cloud to support and shape your long-term business goals. Identify opportunities to optimize technology and business operations, explore new cloud-enabled value propositions and revenue models, and prioritize strategic objectives. Evolve your strategy over time in response to technological advancements and changes in your business environment. Portfolio Management Prioritize cloud products and initiatives in alignment with your strategic intent, operational efficiency, and capacity to deliver. Utilize automated discovery tools and migration strategies (known as the 7 Rs) to rationalize your application portfolio and build a data-driven business case. Balance your cloud portfolio by considering short-term and long-term outcomes, as well as low-risk and higher-risk opportunities. Innovation Management Leverage the cloud to develop and improve processes, products, and experiences. By instantly provisioning and shutting down resources, the cloud can reduce time-to-value and innovation-related costs and risks. Develop an innovation strategy that combines incremental and disruptive initiatives to optimize existing offerings and enable new business models. Implement mechanisms for idea solicitation, selection, and scaling successful innovation pilots. Product Management Manage data- and cloud-enabled offerings as products throughout their lifecycles, delivering repeatable value to internal and external customers. Organize teams around these products to enhance agility and customer-centricity. Establish small, cross-functional teams, identify product owners, define roadmaps, and manage end-to-end lifecycles. Leverage the cloud platform and agile methods to iterate rapidly and reduce dependencies between teams. Strategic Partnership Build or grow your business through strategic partnerships with your cloud provider. These partnerships can help you enhance your cloud expertise, promote your solutions, and drive successful customer engagements. Take advantage of promotional credits, funding benefits, and co-selling opportunities. Leverage your cloud provider's marketplace channel and technical resources to expand reach and mature your cloud-based products and services. Data Monetization Unlock the value of data to achieve measurable business benefits. The cloud enables collection, storage, and analysis of vast amounts of data. Develop a comprehensive data monetization strategy aligned with your strategic intent. Identify opportunities to leverage data and analytics for improving operations, customer and employee experience, decision-making, and enabling new business models. Monetize data internally before exploring external monetization options. Business Insights Gain real-time insights and answer critical business questions. Descriptive insights enable you to track performance, improve decision-making, and optimize operations. Establish cross-functional analytics teams with a deep understanding of the business context. Align analytics efforts with business goals and KPIs. Leverage the Data Catalog, visualization tools, and techniques to discover trends and patterns. Focus on the big picture first and drill down as needed. Data Science Utilize experimentation, advanced analytics, and machine learning to solve complex business problems. Predictive and prescriptive analytics can enhance operational effectiveness, decision-making, and customer and employee experience. Ensure your Data Catalog contains the necessary data products for building and testing machine learning models. Implement CI/CD practices for operational resilience. Understand model predictions and identify potential biases. Deploy models to production and monitor performance. By embracing these business capabilities within the AWS CAF, you can align your cloud investments with your strategic objectives, drive innovation, and unlock the full potential of the cloud to achieve tangible business outcomes. SummaryThe Business Perspective plays a pivotal role in leveraging cloud investments to accelerate digital transformation and drive business success. Embracing the Business Perspective empowers organizations to become more agile, customer-centric, and competitive in the rapidly evolving digital landscape. By leveraging the potential of cloud technologies and adopting a strategic approach to cloud adoption, businesses can drive operational efficiency, improve decision-making, enhance customer experiences, and unlock new revenue opportunities. As we continue our exploration of the AWS CAF, stay tuned for the upcoming articles in this series, where we will delve into the remaining perspectives: People, Governance, Platform, Security, and Operations. Each perspective provides unique insights and strategies that are essential for a successful cloud transformation journey. Cloud adoption frameworks, like the AWS Cloud Adoption Framework (AWS CAF), provide guidance based on best practices and industry experience to help organizations navigate their digital transformation journeys and achieve desired business outcomes using cloud technologies. The AWS CAF serves as a comprehensive resource for organizations looking to digitally transform their operations through the innovative use of AWS. It offers a structured approach to identify and prioritize transformation opportunities, assess cloud readiness, and develop a transformation roadmap that can be iteratively refined over time. Unlocking Business Value through Cloud-Powered Digital TransformationCloud-powered digital transformation involves a series of interconnected processes and capabilities that drive organizational change and deliver business value. By leveraging cloud technologies, organizations can undergo technological, process, organizational, and product transformations, leading to various business outcomes. These outcomes encompass reducing business risks, enhancing environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance, as well as increasing revenue and operational efficiency. Cloud adoption frameworks, like the AWS CAF, provide organizations with a roadmap and set of foundational capabilities to accelerate their digital transformation journeys and achieve these desired outcomes. By employing a comprehensive framework like the AWS CAF, organizations can effectively navigate the path to cloud-powered digital transformation and harness the full potential of cloud technologies to drive business success. Cloud transformation value chain Leveraging Cloud for Technological Transformation When it comes to technological transformation, the focus lies in utilizing the power of the cloud to migrate and modernize legacy infrastructure, applications, and data and analytics platforms. According to Cloud Value Benchmarking, migrating from on-premises to AWS can yield significant benefits. This includes a remarkable 27% reduction in cost per user, a 58% increase in VMs managed per admin, a 57% decrease in downtime, and a 34% decrease in security events. These statistics showcase the potential for cost savings and improved operational efficiency through cloud migration. Driving Process Transformation through Digitization and Automation Process transformation centers around digitizing, automating, and optimizing your business operations. This entails embracing new data and analytics platforms to generate actionable insights and leveraging machine learning (ML) to enhance various aspects of your organization. By employing ML, you can improve customer service experiences, boost employee productivity and decision-making, enhance business forecasting, strengthen fraud detection and prevention, streamline industrial operations, and more. This process optimization can lead to increased operational efficiency, reduced operating costs, and improved experiences for both employees and customers. Reimagining Organizational Dynamics for Transformation Organizational transformation involves reimagining your operating model and how your business and technology teams collaborate to create customer value and fulfill your strategic goals. A key aspect of this transformation is organizing your teams around products and value streams. By adopting agile methods and encouraging rapid iteration and evolution, you can foster a more responsive and customer-centric environment. This shift in organizational dynamics allows for greater adaptability and agility in meeting customer demands and market changes. Revamping Products and Revenue Models for Growth Product transformation revolves around reimagining your business model by developing new value propositions, including products and services, and exploring innovative revenue models. This approach enables you to reach new customers and tap into previously untapped market segments. According to Cloud Value Benchmarking, adopting AWS can lead to a 37% reduction in time-to-market for new features and applications, a significant 342% increase in code deployment frequency, and a notable 38% reduction in the time required to deploy new code. These statistics highlight the potential for accelerated innovation and market responsiveness through the adoption of AWS. By embracing the various facets of transformation outlined above—technological, process, organizational, and product—you can propel your organization forward, leveraging the cloud to unlock new possibilities and achieve your desired business outcomes. Foundational CapabilitiesTo enable each transformation domain discussed earlier, a set of foundational capabilities is essential. These capabilities serve as the building blocks for achieving desired outcomes. The figure below illustrates these foundational capabilities. In simple terms, a capability refers to an organizational ability to utilize processes and resources, including people, technology, and other assets, to accomplish specific goals. In the context of AWS Cloud Adoption Framework (AWS CAF), these capabilities offer best practice guidance to enhance your cloud readiness, ensuring effective utilization of the cloud for digital transformation. AWS CAF organizes these capabilities into six perspectives: Business, People, Governance, Platform, Security, and Operations. Each perspective encompasses a collection of capabilities that are owned or managed by stakeholders associated with your cloud transformation journey. AWS CAF perspectives and foundational capabilities Business Perspective The Business perspective aims to ensure that your cloud investments align with your digital transformation goals and contribute to overall business outcomes. Key stakeholders in this perspective include the CEO, CFO, COO, CIO, and CTO. Their involvement is crucial in leveraging cloud technologies to drive strategic initiatives and achieve desired business results. People Perspective The People perspective acts as a bridge between technology and business, accelerating the cloud journey and facilitating a culture of continuous growth and learning. It focuses on aspects such as organizational culture, structure, leadership, and workforce development. Key stakeholders in this perspective include the CIO, COO, CTO, cloud director, and cross-functional leaders across the organization. Governance Perspective The Governance perspective plays a vital role in orchestrating your cloud initiatives while maximizing organizational benefits and mitigating transformation-related risks. It involves stakeholders such as the chief transformation officer, CIO, CTO, CFO, CDO, and CRO. Their involvement ensures that proper governance mechanisms are in place to guide decision-making, compliance, and risk management throughout the cloud transformation journey. Platform Perspective The Platform perspective focuses on building an enterprise-grade, scalable, hybrid cloud platform. It encompasses modernizing existing workloads and implementing new cloud-native solutions. Key stakeholders in this perspective include the CTO, technology leaders, architects, and engineers who play a crucial role in designing and implementing an effective cloud platform. Security Persepctive The Security perspective is dedicated to achieving the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data and cloud workloads. It involves stakeholders such as the CISO, CCO, internal audit leaders, and security architects and engineers. Their expertise ensures that robust security measures are in place to protect data and maintain compliance with relevant regulations. Operations Persepctive The Operations perspective focuses on delivering cloud services that meet the needs of your business. It involves stakeholders such as infrastructure and operations leaders, site reliability engineers, and IT service managers. Their efforts ensure the smooth functioning of cloud services and efficient management of operational processes. By understanding and effectively leveraging these foundational capabilities across the various perspectives, organizations can drive successful cloud-powered transformations and achieve their desired business outcomes. Embarking on Your Cloud Transformation JourneyEvery organization's journey to the cloud is unique. To ensure the success of your transformation, it is essential to have a clear vision of your desired target state, evaluate your cloud readiness, and embrace an agile approach to bridge any gaps that may arise. By adopting an incremental and iterative strategy, you can quickly demonstrate value while avoiding the need to make extensive predictions. This iterative approach allows you to maintain momentum and adapt your roadmap based on the valuable insights gained through experience. The AWS Cloud Adoption Framework (AWS CAF) recommends four distinct phases for your cloud transformation journey, as illustrated below. Cloud transformation journey Phase 1: Envision During the Envision phase, the focus is on showcasing how the cloud can accelerate your business outcomes. This involves identifying and prioritizing transformation opportunities across the four transformation domains in alignment with your strategic business objectives. By associating your transformation initiatives with key stakeholders who possess the influence and ability to drive change, and by emphasizing measurable business outcomes, you can effectively demonstrate the value of your transformation journey as you progress. Phase 2: Align The Align phase revolves around identifying capability gaps across the six perspectives of the AWS CAF. It involves recognizing cross-organizational dependencies and addressing stakeholder concerns and challenges. This phase helps you develop strategies to enhance your cloud readiness, ensure stakeholder alignment, and facilitate relevant organizational change management activities. By focusing on these foundational aspects, you establish a solid footing for your cloud transformation journey. Phase 3: Launch The Launch phase emphasizes delivering pilot initiatives in a production environment to showcase incremental business value. These pilots should be carefully selected for their significant impact and potential to influence future directions. Learning from these pilot projects allows you to make necessary adjustments before scaling up to full production, ensuring a smoother transition and minimizing risks. Phase 4: Scale The Scale phase is all about expanding production pilots and fully realizing the business benefits associated with your cloud investments. The goal is to extend the demonstrated value to the desired scale and ensure its sustainability. By gradually increasing the scope of your cloud initiatives and leveraging the lessons learned along the way, you can effectively amplify the positive impact on your organization. It's important to note that you don't have to tackle all the foundational capabilities at once. As you progress through your cloud transformation journey, you can evolve these capabilities and improve your cloud readiness accordingly. Consider tailoring the suggested sequence depicted in the figure to suit your organization's specific needs and priorities. This flexibility allows you to navigate your transformation journey with agility and customization, ensuring a successful transition to the cloud. Evolution of AWS CAF perspectives and foundational capabilities SummaryIn conclusion, embarking on a cloud transformation journey is a significant undertaking for any organization. By leveraging the AWS Cloud Adoption Framework (AWS CAF) and following the iterative and incremental approach, you can successfully navigate this journey and unlock the full potential of the cloud. Envisioning your desired target state, aligning capabilities, launching pilot initiatives, and scaling up to achieve business value are essential phases that contribute to a smooth and impactful transformation. As you progress through your cloud transformation, it's crucial to consider the unique needs and priorities of your organization. Tailoring the foundational capabilities and sequence of activities outlined in the AWS CAF to your specific requirements will allow for a more customized and effective transformation. Remember, this journey is not a one-size-fits-all approach, but rather a dynamic process that evolves with your organization's goals and aspirations. Building upon the foundations discussed in this article, we will now delve into a series of articles that explore each of the six AWS CAF perspectives or pillars. These perspectives - Business, People, Governance, Platform, Security, and Operations - play vital roles in shaping your cloud transformation and ensuring its success. Stay tuned for our upcoming series, where we will provide in-depth insights into each AWS CAF perspective. From aligning cloud investments with strategic business objectives to establishing robust security measures, we will guide you through the intricacies of these perspectives and equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions along your cloud transformation journey. These decisions have the potential to impact an organization's scalability and its ability to enhance the environment in the future. To simplify this complexity, customers are actively seeking prescriptive guidance across a wide range of AWS services that can be utilized to create a solid foundational environment. The key to establishing a successful cloud foundation on AWS lies in tailoring the guidance to the unique business needs of each organization. By adopting a capability-based approach, organizations can create an environment that enables them to efficiently deploy, operate, and govern their workloads. Furthermore, this approach allows them to enhance their capabilities and expand their environment as their requirements evolve and additional workloads are deployed to the cloud. A standardized, prescriptive set of capabilities spanning different functional areas can serve as a structured approach for swiftly building or expanding an AWS Cloud environment. Organizations can adopt and implement these capabilities based on their operational and governance needs. As their business requirements mature, the capability-based approach can be utilized to ensure that their cloud environment is prepared to support their workloads and scale accordingly. Cloud Foundations To address these needs, AWS has created Cloud Foundations which provides a guided path to help organisations deploy, configure, and secure their new workloads while ensuring they are ready for on-going operations in the cloud. Using Cloud Formations can help support your cloud foundation journey, accelerating the deployment of a production-ready environment. When it comes to embracing the cloud, AWS advises having a solid set of foundational capabilities that empower you to effortlessly deploy, manage, and govern your workloads. These capabilities serve as the building blocks for establishing and operating various aspects of your cloud environment. Think of them as the tools and guidelines that assist you in planning, implementing, and effectively running your cloud infrastructure. They encompass considerations for people, processes, and technology, seamlessly integrating with your overall technology ecosystem. But it's not just about the technical implementation. These capabilities also encompass operational guidance, ensuring you have the necessary resources and skills to set up and maintain each capability. This includes notifications, event handling, remediation processes, and the expertise of your team members. In other words, it's all about equipping you with the knowledge and support needed to successfully leverage each capability. So, whether you're diving into the cloud for the first time or enhancing your existing environment, these foundational capabilities and categories provide you with a comprehensive framework to navigate the complexities of cloud adoption. With their guidance and automation, you can confidently establish and operate a robust cloud environment that meets your specific needs and helps you achieve your business goals. AWS has defined a set of 30 capabilities that span six categories to help you establish a cloud foundation. Table 1: Cloud Foundations capabilities by categories Each capability includes stages of maturity that enable you to implement based on where you are in your cloud journey, including your governance and operational requirements. As your cloud environment grows and matures, the capabilities can be enhanced to meet your new requirements. Capabilities DefinitionsThis section includes high-level definitions for each foundational capability organized by their category as shown in the figure below. Figure 1: Cloud Foundations Categories Governance, Risk Management, and ComplianceWhen it comes to Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (GRC), it's all about establishing a solid foundation for meeting security and compliance requirements while defining the policies that should govern your cloud environment. These capabilities play a crucial role in determining what needs to be done, defining your risk tolerance, and ensuring alignment with internal policies. Figure 2: Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance Category Within the Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance category, you'll find a range of capabilities designed to empower you in your GRC efforts:
These capabilities within the Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance category offer you the necessary tools and guidance to establish a secure and compliant cloud environment. By leveraging them effectively, you can confidently navigate the complexities of GRC and safeguard your organization's interests. Operations When it comes to Operations, the goal is to enable your developers and operations teams to innovate at a rapid pace while maintaining the quality of application and infrastructure updates. The capabilities within this category empower you to effortlessly build, deploy, and operate workloads in the cloud, enhancing the developer experience and leveraging powerful tools. Figure 3: Operations Category Let's explore the capabilities within the Operations category that can revolutionize the way you manage your cloud environment:
With these Operations capabilities at your disposal, you can revolutionize how you manage your cloud environment. By enhancing the developer experience, ensuring effective rollout and rollback strategies, implementing robust logging and monitoring, simplifying resource management, and keeping your systems patched, you can drive efficiency, reliability, and innovation throughout your operations. Security When it comes to Security, the focus is on creating a secure, high-performing, and resilient foundation for your cloud environment. The capabilities within this category allow you to design and implement robust security policies and controls at different levels of the stack, protecting your valuable resources from both external and internal vulnerabilities and threats. These capabilities ensure confidentiality, availability, integrity, and usability, while providing guidance and recommendations for effective remediation. Figure 4: Security Category Let's delve into the capabilities within the Security category that empower you to establish a strong and reliable security framework for your cloud environment:
By leveraging these Security capabilities, you can establish a robust security framework for your cloud environment, safeguarding your resources, and mitigating risks. From identity management and access control to data isolation, application security, encryption and key management, secrets management, incident response, and vulnerability management, these capabilities provide a comprehensive approach to protecting your cloud environment from a wide range of threats and vulnerabilities. Business ContinuityWhen it comes to Business Continuity, resilience is key as it directly impacts the quality of service your users experience. The capabilities within this category empower you to establish a comprehensive strategy to ensure the continuity of operations during times of inefficiency or crisis. By implementing Disaster Recovery, Backups, and Support, you can proactively mitigate the impact of disruptions, minimize downtime during outages, and navigate unprecedented situations more effectively. Figure 5: Business Continuity Category Let's explore the capabilities within the Business Continuity category that enable you to maintain uninterrupted operations and mitigate potential disruptions:
By leveraging these Business Continuity capabilities, you can establish a resilient foundation that ensures the continuity of your operations, even in the face of disruptions. Whether it's implementing robust backup strategies, enabling efficient Disaster Recovery processes, or having reliable support mechanisms, these capabilities enable you to navigate challenges and maintain business continuity. Proactively addressing potential inefficiencies and preparing for unforeseen events can help you avoid downtime, minimize service disruptions, and ultimately deliver a seamless experience to your users. FinanceWhen it comes to Finance, it's essential to establish and enhance your existing finance processes to be cloud-ready. By leveraging the capabilities within this area, you can effectively manage costs, ensure transparency and control, optimize spending, and meet compliance and regulatory requirements. Additionally, these capabilities enable you to efficiently manage your records and resource inventory, ensuring accurate financial management within your cloud environment. Figure 6: Finance Category Let's explore the capabilities within the Finance category that empower you to establish robust financial processes and optimize your cloud operations:
By leveraging these Finance capabilities, you can establish a cloud-ready finance framework that promotes cost transparency, control, planning, and optimization. From effectively managing variable expenses to maintaining accurate resource inventories and meeting regulatory requirements, these capabilities provide the foundation for efficient financial operations within your cloud environment. By embracing cloud financial management, resource inventory management, and records management, you can drive financial efficiency, ensure compliance, and optimize your cloud investments. InfrastructureWhen it comes to Infrastructure, it's crucial to design, build, and manage a secure and highly available cloud infrastructure. By leveraging the capabilities within this area, you can ensure the reliability and security of your infrastructure while accommodating the migration of applications from on-premises environments or building them natively in the cloud. Let's explore the key capabilities within the Infrastructure category that empower you to create a robust and resilient cloud infrastructure. Figure 7: Infrastructure Category
By leveraging these Infrastructure capabilities, you can design, build, and manage a secure and highly available cloud infrastructure. From implementing robust network security measures to ensuring reliable network connectivity, template management, and workload isolation, these capabilities provide the foundation for a secure and scalable infrastructure. By prioritizing infrastructure security and reliability, you can create a resilient environment that supports the migration and development of applications in the cloud with confidence. SummaryIn today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, establishing a solid foundation for your cloud environment is essential. The capabilities within different categories, such as Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance; Operations; Security; Business Continuity; Finance; and Infrastructure, enable organizations to leverage the full potential of the cloud while ensuring security, efficiency, and resilience. By strategically leveraging these capabilities, organizations can design, build, and manage their cloud environment with confidence. From defining policies and managing risks to optimizing costs, securing applications, ensuring business continuity, and establishing a robust infrastructure, these capabilities provide the necessary tools and frameworks to navigate the complexities of the cloud.
In the previous two articles on Cloud Migration Strategy and Best Practices, we discussed the importance of having a well-defined strategy, a clear scope, and realistic timeline for successful cloud migration projects. We also highlighted the critical role that people and technology play in the success of cloud migration projects. In this article, we will shift our focus to the process perspective of cloud migration in terms of preparing for a large migration and running a large migration. Process PerspectiveWhen it comes to large-scale migrations, having a well-defined process in place is critical. While processes bring consistency, they must also be adaptable to each project's unique requirements. Running the process repeatedly will help you identify gaps and areas for improvement, leading to significant benefits as you iterate, learn, and adopt new ideas. Managing processes in migrations can be challenging as they often span multiple technologies and boundaries that may not have been linked before. This guide provides processes and guidance on specific requirements for large migrations, helping you achieve success while maintaining quality and team confidence. Preparing for a Large MigrationTo ensure a successful migration journey, it is crucial to establish core principles that provide a clear direction and obtain buy-in from stakeholders. In this section, we will cover the following topics:
Define Business Drivers and Communicate Strategy, Scope and Timeline Defining business drivers and having a clear communication plan for the straetgy, scope and timeline are vital for large migrations to AWS. Different migration paths can be considered, such as rehosting workloads, containerizing applications, or redesigning them into serverless architecture. To determine the appropriate migration path, it is important to align with business drivers. Involving various stakeholders, including application owners, network teams, database administrators, and executive sponsors, is crucial. Documenting business drivers and setting key performance indicators (KPIs) aligned with target outcomes helps ensure stakeholder alignment and effective decision-making. Define a Clear Escalation Path to Help Remove Blockers Large cloud migration programs involve multiple stakeholders with their own priorities, which can create challenges. To address this, a clear escalation path must be established to outline the necessary actions for removing any blockers that may arise. This streamlines decision-making processes and ensures alignment among teams. An example of resolving conflicting migration paths is setting a clear mandate following an escalation to the Chief Information Officer (CIO) and implementing a mechanism for requesting required decisions. Minimize Unnecessary Change While change is beneficial, excessive changes can introduce additional risks. When a business case for a large migration is approved, it is recommended to set a two-week rule to prevent application teams from spending excessive time rewriting their applications. This rule helps maintain consistency and enables a sustainable migration process over a multi-year period. By minimizing changes that do not align with the desired business outcomes, mechanisms can be developed to manage such changes in future projects. Document an End-to-End Process Early Comprehensive documentation of the entire migration process is essential for effective planning. This documentation should assign ownership of tasks and processes to specific stakeholders, ensuring clarity of roles and responsibilities. It also helps identify potential issues and facilitates ongoing improvements. Existing processes, dependencies, and integration points should be documented, and a RACI matrix can be created to assign responsibilities and accountabilities. Additionally, establishing a countdown plan, working backward from the workload migration cutover date and time, provides a structured approach. Document Standard Migration Patterns and Artifacts Documenting standard migration patterns and artifacts is critical for success. These resources serve as reusable references, documentation, and runbooks for future migration projects, enabling avoidance of past pitfalls and issues. Standard processes and artifacts significantly accelerate the migration process and improve consistency. It is recommended to establish central ownership of these documents and artifacts, with a process for submitting recommended changes. Regularly sharing updates and changes with all teams promotes effective communication and ensures consistency throughout the migration project. Establish a Single Source of Truth for Migration Metadata and Status Creating a single source of truth for migration metadata and status is essential for effective planning. This allows all teams to align and make data-driven decisions. Initially, multiple data sources may exist, such as configuration management databases (CMDBs) or inventory lists. Data capture mechanisms, like using discovery tooling or surveying IT leaders, may be necessary. Aggregating all data sources into a single dataset simplifies tracking the migration progress, including the status of migrated servers. Running a Large MigrationOnce the business outcomes have been established and the migration strategy has been communicated to the stakeholders, it is time to plan how to divide the scope of the large migration into manageable migration events or waves. The following sections provide essential guidance for creating a wave plan. Plan Migration Waves Ahead of Time to Ensure a Steady Flow Thorough planning is crucial for the success of the migration program. Planning migration waves in advance allows the project to progress smoothly and enables the team to be proactive in addressing migration requirements. It facilitates scalability, enhances decision-making, and improves forecasting as project demands become more complex. Additionally, planning ahead enhances the team's adaptability to changes. For instance, a financial services customer working on a data center exit program initially faced delays due to sequential wave planning. When stakeholders were informed about their applications' migration to AWS, they still had several tasks to complete before starting the migration, causing significant program delays. To address this, the customer implemented a holistic approach where migration waves were planned months in advance. This provided ample time for application teams to complete pre-migration activities and eliminated unnecessary delays. Keep Wave Implementation and Wave Planning Separate Separating the teams responsible for wave planning and wave implementation allows both processes to work concurrently. With effective communication and coordination, this approach avoids slowdowns in the migration caused by insufficiently prepared servers or applications. It is crucial to involve the migration implementation team during wave planning to ensure complete and accurate data collection. Additionally, creating a buffer between wave preparation and implementation is essential. Collaboration between the wave planning team and the migration team is necessary to gather the right data and minimize the need for rework. Start Small for Great Outcomes Starting with a small-scale initial wave and gradually increasing migration velocity in subsequent waves leads to favorable outcomes. The first wave should involve a single, small application with fewer than 10 servers. As the migration progresses, additional applications and servers can be included in subsequent waves, gradually building up to the target migration velocity. Prioritizing less complex or risky applications and incrementally ramping up the migration velocity allows the team to adjust to working together and learn from the process. With each wave, the team can identify and implement process improvements, significantly enhancing the velocity of later waves. For example, a customer migrating over 1,300 servers in a year began with a pilot migration and a few smaller waves. This approach allowed the team to identify opportunities for improvement, optimize network segments, collaborate with the firewall team to prevent delays, and develop automation scripts for discovery and cutover processes. Starting small enabled the team to focus on process enhancements and increased overall confidence. Minimize the Number of Cutover Windows Maintaining discipline in managing scale is crucial for successful mass migrations. Limiting the number of weekly cutover windows ensures that the time spent on cutover activities is maximized. By reducing flexibility in this area, unnecessary delays and operational burdens associated with scheduling are minimized. For instance, instead of having multiple small cutovers, consolidating servers into fewer, larger cutovers optimizes operational efficiency and reduces potential delays. A large technology company experienced delays early in their migration project due to application teams having the flexibility to dictate migration schedules until the last minute. This resulted in constant negotiation and stress for the migration team. To address this, the company improved their planning discipline and reduced the number of cutover windows, avoiding delays in meeting data center contract expiration dates. Fail Fast, Apply Experience, and Iterate It is common for initial migration waves to encounter challenges and setbacks. Failing early in the process allows the team to learn, identify bottlenecks, and apply lessons learned to subsequent waves. During the initial stages of a migration, the team needs time to adjust, integrate various tools and people, and continuously improve the end-to-end process. Understanding and communicating that initial issues are expected is crucial, as some teams may be reluctant to embrace new approaches and failure. Ensuring everyone understands that these challenges are part of the journey encourages the team to learn, adapt, and ultimately achieve a successful migration. For instance, a company planning to migrate over 10,000 servers in 24-36 months began with learning waves to understand the processes and permissions involved. Through iterative improvements, such as integrating with CMDB and CyberArk, the team increased their migration velocity to over 120 servers per week within six months. Don't Forget the Retrospective Conducting retrospectives is an essential part of an agile process. These sessions allow the team to reflect, discuss, learn, and make necessary adjustments before moving forward. Retrospectives provide a structured approach to capturing lessons learned, which can then be used to drive improvements. For large migrations to succeed, constant evolution and improvement of processes, tools, and teams are vital. Retrospectives play a significant role in this continuous improvement cycle. Instead of waiting until the end of the program, lessons learned from previous waves should be applied to the planning of subsequent waves. Regular retrospectives provide opportunities to identify areas for streamlining, process improvements, and automation. By implementing a countdown schedule and automating manual tasks, one customer significantly minimized delays and optimized their cutover process. Another large tech company held regular retrospectives that led to improvements in processes, scripts, and automation, resulting in a 40% reduction in average migration time over the course of the program. ConclusionLarge migrations present different challenges when compared to smaller migrations. This is mostly due to the complexities introduced by the scale. Running a large migration requires meticulous planning and execution as well as effective coordination, and a focus on continuous improvement. By following the guidance provided in this three-part series, organizations can navigate the complexities of large-scale migrations and achieve successful outcomes.
|
AuthorTim Hardwick is a Strategy & Transformation Consultant specialising in Technology Strategy & Enterprise Architecture Archives
June 2023
Categories
All
|
Site powered by Weebly. Managed by iPage