|
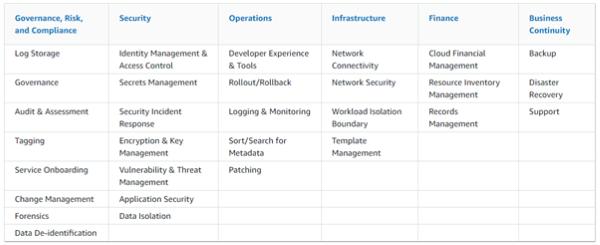
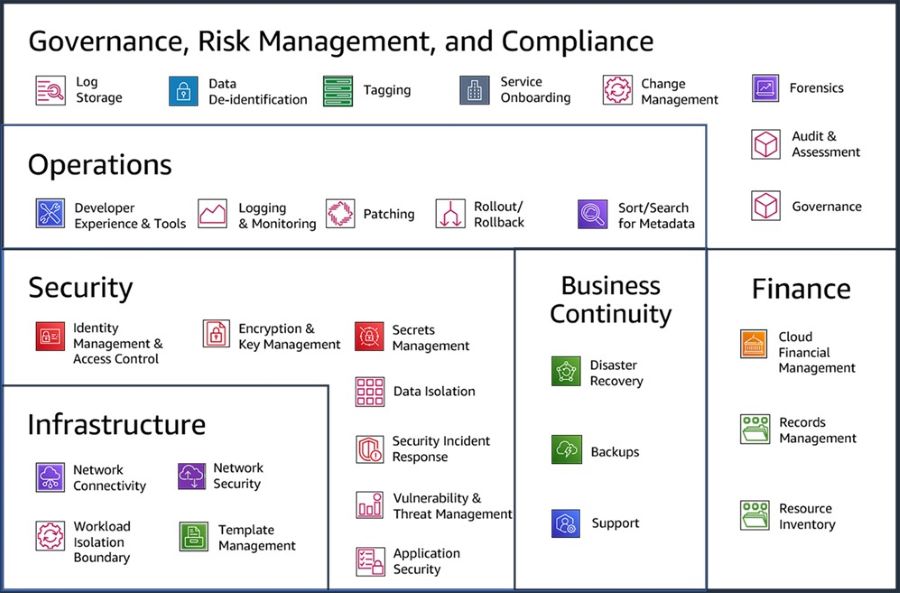
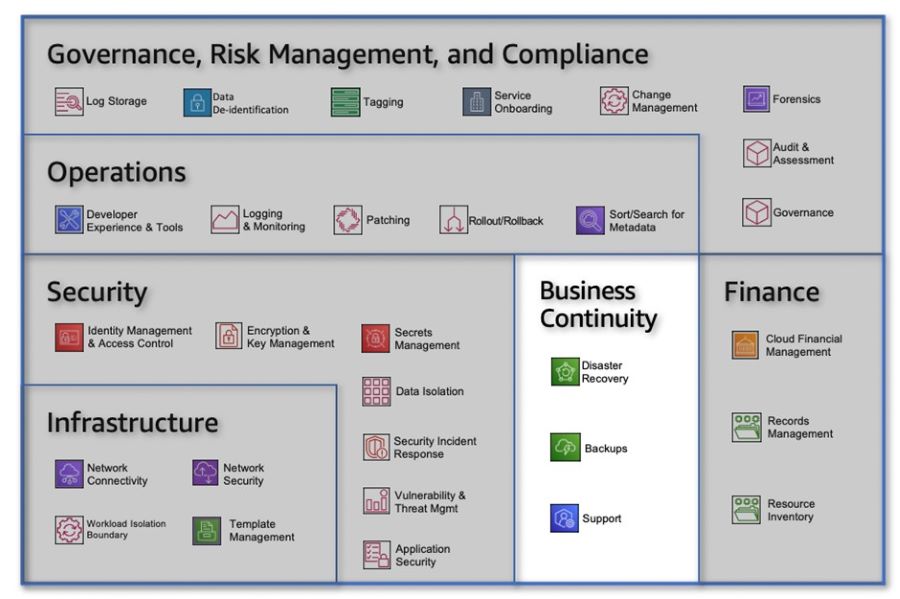
These decisions have the potential to impact an organization's scalability and its ability to enhance the environment in the future. To simplify this complexity, customers are actively seeking prescriptive guidance across a wide range of AWS services that can be utilized to create a solid foundational environment. The key to establishing a successful cloud foundation on AWS lies in tailoring the guidance to the unique business needs of each organization. By adopting a capability-based approach, organizations can create an environment that enables them to efficiently deploy, operate, and govern their workloads. Furthermore, this approach allows them to enhance their capabilities and expand their environment as their requirements evolve and additional workloads are deployed to the cloud. A standardized, prescriptive set of capabilities spanning different functional areas can serve as a structured approach for swiftly building or expanding an AWS Cloud environment. Organizations can adopt and implement these capabilities based on their operational and governance needs. As their business requirements mature, the capability-based approach can be utilized to ensure that their cloud environment is prepared to support their workloads and scale accordingly. Cloud Foundations To address these needs, AWS has created Cloud Foundations which provides a guided path to help organisations deploy, configure, and secure their new workloads while ensuring they are ready for on-going operations in the cloud. Using Cloud Formations can help support your cloud foundation journey, accelerating the deployment of a production-ready environment. When it comes to embracing the cloud, AWS advises having a solid set of foundational capabilities that empower you to effortlessly deploy, manage, and govern your workloads. These capabilities serve as the building blocks for establishing and operating various aspects of your cloud environment. Think of them as the tools and guidelines that assist you in planning, implementing, and effectively running your cloud infrastructure. They encompass considerations for people, processes, and technology, seamlessly integrating with your overall technology ecosystem. But it's not just about the technical implementation. These capabilities also encompass operational guidance, ensuring you have the necessary resources and skills to set up and maintain each capability. This includes notifications, event handling, remediation processes, and the expertise of your team members. In other words, it's all about equipping you with the knowledge and support needed to successfully leverage each capability. So, whether you're diving into the cloud for the first time or enhancing your existing environment, these foundational capabilities and categories provide you with a comprehensive framework to navigate the complexities of cloud adoption. With their guidance and automation, you can confidently establish and operate a robust cloud environment that meets your specific needs and helps you achieve your business goals. AWS has defined a set of 30 capabilities that span six categories to help you establish a cloud foundation. Table 1: Cloud Foundations capabilities by categories Each capability includes stages of maturity that enable you to implement based on where you are in your cloud journey, including your governance and operational requirements. As your cloud environment grows and matures, the capabilities can be enhanced to meet your new requirements. Capabilities DefinitionsThis section includes high-level definitions for each foundational capability organized by their category as shown in the figure below. Figure 1: Cloud Foundations Categories Governance, Risk Management, and ComplianceWhen it comes to Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (GRC), it's all about establishing a solid foundation for meeting security and compliance requirements while defining the policies that should govern your cloud environment. These capabilities play a crucial role in determining what needs to be done, defining your risk tolerance, and ensuring alignment with internal policies. Figure 2: Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance Category Within the Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance category, you'll find a range of capabilities designed to empower you in your GRC efforts:
These capabilities within the Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance category offer you the necessary tools and guidance to establish a secure and compliant cloud environment. By leveraging them effectively, you can confidently navigate the complexities of GRC and safeguard your organization's interests. Operations When it comes to Operations, the goal is to enable your developers and operations teams to innovate at a rapid pace while maintaining the quality of application and infrastructure updates. The capabilities within this category empower you to effortlessly build, deploy, and operate workloads in the cloud, enhancing the developer experience and leveraging powerful tools. Figure 3: Operations Category Let's explore the capabilities within the Operations category that can revolutionize the way you manage your cloud environment:
With these Operations capabilities at your disposal, you can revolutionize how you manage your cloud environment. By enhancing the developer experience, ensuring effective rollout and rollback strategies, implementing robust logging and monitoring, simplifying resource management, and keeping your systems patched, you can drive efficiency, reliability, and innovation throughout your operations. Security When it comes to Security, the focus is on creating a secure, high-performing, and resilient foundation for your cloud environment. The capabilities within this category allow you to design and implement robust security policies and controls at different levels of the stack, protecting your valuable resources from both external and internal vulnerabilities and threats. These capabilities ensure confidentiality, availability, integrity, and usability, while providing guidance and recommendations for effective remediation. Figure 4: Security Category Let's delve into the capabilities within the Security category that empower you to establish a strong and reliable security framework for your cloud environment:
By leveraging these Security capabilities, you can establish a robust security framework for your cloud environment, safeguarding your resources, and mitigating risks. From identity management and access control to data isolation, application security, encryption and key management, secrets management, incident response, and vulnerability management, these capabilities provide a comprehensive approach to protecting your cloud environment from a wide range of threats and vulnerabilities. Business ContinuityWhen it comes to Business Continuity, resilience is key as it directly impacts the quality of service your users experience. The capabilities within this category empower you to establish a comprehensive strategy to ensure the continuity of operations during times of inefficiency or crisis. By implementing Disaster Recovery, Backups, and Support, you can proactively mitigate the impact of disruptions, minimize downtime during outages, and navigate unprecedented situations more effectively. Figure 5: Business Continuity Category Let's explore the capabilities within the Business Continuity category that enable you to maintain uninterrupted operations and mitigate potential disruptions:
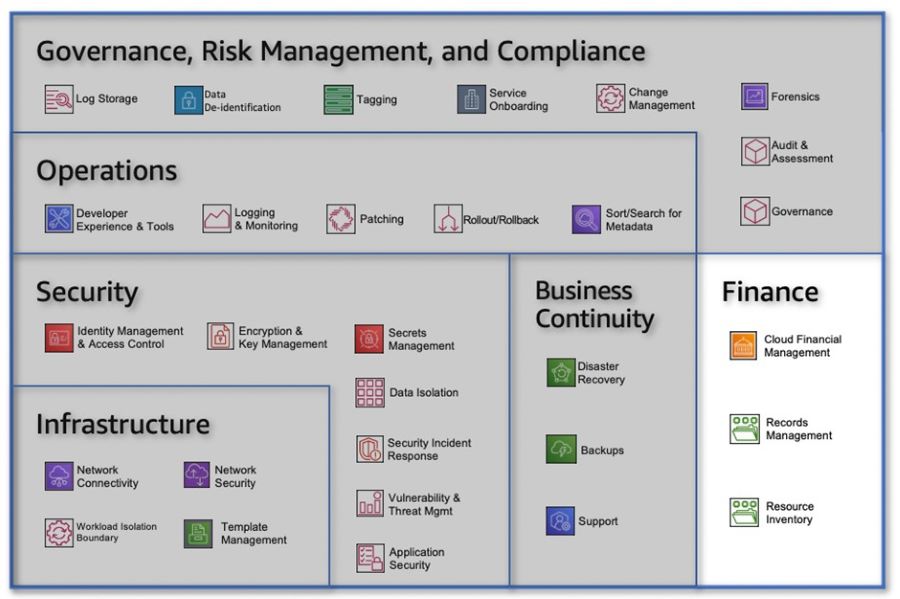
By leveraging these Business Continuity capabilities, you can establish a resilient foundation that ensures the continuity of your operations, even in the face of disruptions. Whether it's implementing robust backup strategies, enabling efficient Disaster Recovery processes, or having reliable support mechanisms, these capabilities enable you to navigate challenges and maintain business continuity. Proactively addressing potential inefficiencies and preparing for unforeseen events can help you avoid downtime, minimize service disruptions, and ultimately deliver a seamless experience to your users. FinanceWhen it comes to Finance, it's essential to establish and enhance your existing finance processes to be cloud-ready. By leveraging the capabilities within this area, you can effectively manage costs, ensure transparency and control, optimize spending, and meet compliance and regulatory requirements. Additionally, these capabilities enable you to efficiently manage your records and resource inventory, ensuring accurate financial management within your cloud environment. Figure 6: Finance Category Let's explore the capabilities within the Finance category that empower you to establish robust financial processes and optimize your cloud operations:
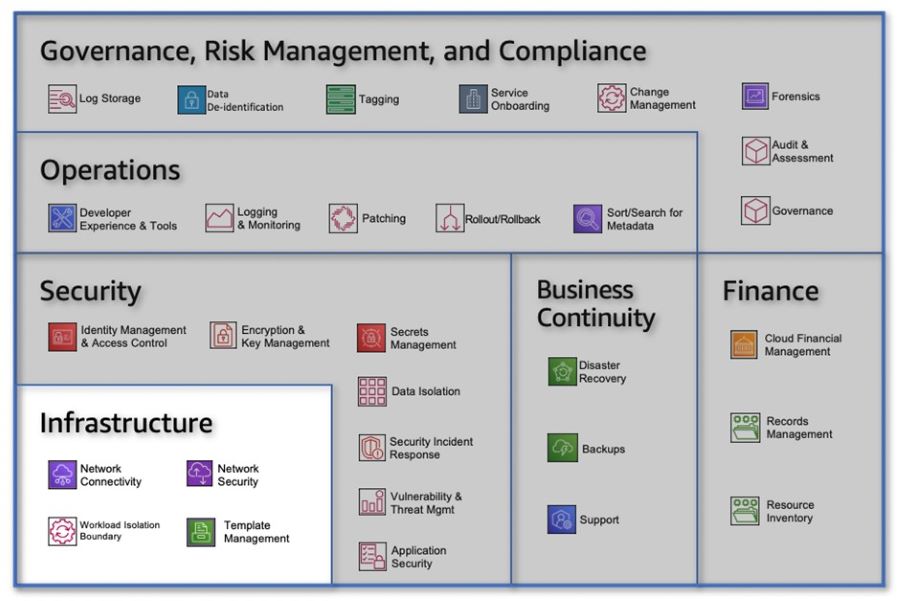
By leveraging these Finance capabilities, you can establish a cloud-ready finance framework that promotes cost transparency, control, planning, and optimization. From effectively managing variable expenses to maintaining accurate resource inventories and meeting regulatory requirements, these capabilities provide the foundation for efficient financial operations within your cloud environment. By embracing cloud financial management, resource inventory management, and records management, you can drive financial efficiency, ensure compliance, and optimize your cloud investments. InfrastructureWhen it comes to Infrastructure, it's crucial to design, build, and manage a secure and highly available cloud infrastructure. By leveraging the capabilities within this area, you can ensure the reliability and security of your infrastructure while accommodating the migration of applications from on-premises environments or building them natively in the cloud. Let's explore the key capabilities within the Infrastructure category that empower you to create a robust and resilient cloud infrastructure. Figure 7: Infrastructure Category
By leveraging these Infrastructure capabilities, you can design, build, and manage a secure and highly available cloud infrastructure. From implementing robust network security measures to ensuring reliable network connectivity, template management, and workload isolation, these capabilities provide the foundation for a secure and scalable infrastructure. By prioritizing infrastructure security and reliability, you can create a resilient environment that supports the migration and development of applications in the cloud with confidence. SummaryIn today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, establishing a solid foundation for your cloud environment is essential. The capabilities within different categories, such as Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance; Operations; Security; Business Continuity; Finance; and Infrastructure, enable organizations to leverage the full potential of the cloud while ensuring security, efficiency, and resilience. By strategically leveraging these capabilities, organizations can design, build, and manage their cloud environment with confidence. From defining policies and managing risks to optimizing costs, securing applications, ensuring business continuity, and establishing a robust infrastructure, these capabilities provide the necessary tools and frameworks to navigate the complexities of the cloud.
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
AuthorTim Hardwick is a Strategy & Transformation Consultant specialising in Technology Strategy & Enterprise Architecture Archives
June 2023
Categories
All
|
Site powered by Weebly. Managed by iPage